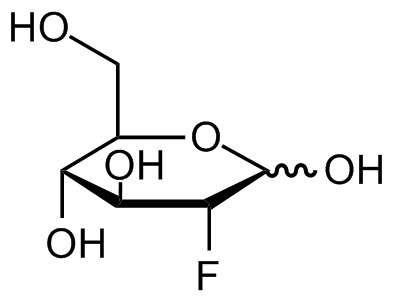
Chemical Structure
2-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose [29702-43-0]
CDX-F0076
CAS Number29702-43-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight182.15
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product Name2-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose [29702-43-0]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number29702-43-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Molecular FormulaC6H11FO5
- Molecular Weight182.15
- Scientific Description2-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose [FDG] is a glucose analog that inhibits cellular glycosylation. It is the natural isotope-form of 18F-FDG that can be taken up by cells but does not undergo metabolic glycolysis. FDG uptake is closely related to the expression of the glucose transporter (GLUT) in malignant tumours. FDG is also a substrate of hexokinase isozymes and an inhibitor of cellular glycosylation. FDG is taken up by high-glucose-using cells such as brain, brown adipocytes, kidney and cancer cells, where phosphorylation prevents the glucose from being released again from the cell, once it has been absorbed. The 2-hydroxyl group (-OH) in normal glucose is needed for further glycolysis (metabolism of glucose by splitting it), but FDG is missing this 2-hydroxyl and cannot be further metabolized in cells. FDG is used in positron emission tomography (PET) as contrast agent and is the most widely used PET marker. FDG-PET can be used for diagnosis, staging, and monitoring treatment of cancers, particularly in Hodgkins disease, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, and lung cancer. FDG has also anticancer and chemosensitizing activity. - Chemical. CAS: 29702-43-0. Formula: C6H11FO5. MW: 182.15. 2-Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose [FDG] is a glucose analog that inhibits cellular glycosylation. It is the natural isotope-form of 18F-FDG that can be taken up by cells but does not undergo metabolic glycolysis. FDG uptake is closely related to the expression of the glucose transporter (GLUT) in malignant tumours. FDG is also a substrate of hexokinase isozymes and an inhibitor of cellular glycosylation. FDG is taken up by high-glucose-using cells such as brain, brown adipocytes, kidney and cancer cells, where phosphorylation prevents the glucose from being released again from the cell, once it has been absorbed. The 2-hydroxyl group (-OH) in normal glucose is needed for further glycolysis (metabolism of glucose by splitting it), but FDG is missing this 2-hydroxyl and cannot be further metabolized in cells. FDG is used in positron emission tomography (PET) as contrast agent and is the most widely used PET marker. FDG-PET can be used for diagnosis, staging, and monitoring treatment of cancers, particularly in Hodgkins disease, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, and lung cancer. FDG has also anticancer and chemosensitizing activity.
- SMILESO[C@H]1C(F)C(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

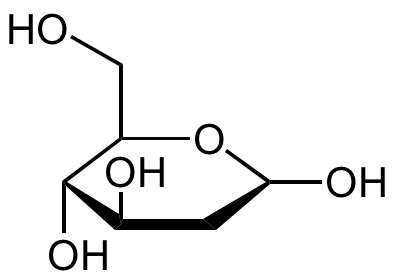
![2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-Glucose [29702-43-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/67/CgoaEGayHkiESgucAAAAALblRiI985.png)