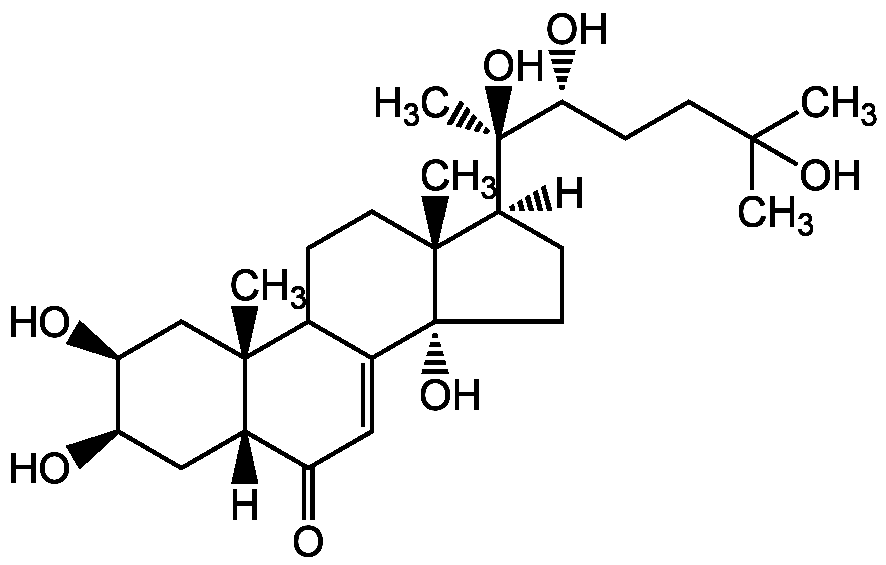
Chemical Structure
20-Hydroxyecdysone
AG-CN2-0072
CAS Number5289-74-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight480.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name20-Hydroxyecdysone
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number5289-74-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC27H44O7
- Molecular Weight480.6
- Scientific DescriptionA member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. More potent than ecdysone. Induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires, and it causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Plays a key role in insect development, cell proliferaton, growth and apoptosis by controlling gene expression involved in moulting and metamorphosis. It acts through a heterodimeric receptor comprising the ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle proteins (USP). Regulates lipolysis in insects. Appears in many plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. Used for controlled gene expression in scientific research, agriculture and medicine. Used for the development of selective insect growth regulators for use as environmentally benign insecticides. Shows biological effects on mammalian species. Neurosteroid. Antiepileptic. Acts on the modulatory site of the GABAA receptor and potentiates GABAergic inhibition in rat. Was shown to stimulate and modulate neutrophil production. Antidiabetic and antiobesity. Could be used as a nutritional supplement for the prevention and treatment of obesity and obesity-associated disorders. May protect PC12 cells against CoCl(2)-induced cell injury by inhibiting ROS production and modulating components of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Does not have potent anabolic properties, however, a muscle-specific increase is observed and genes are identified to provide an explanation for the muscle accretion. Potential fibrosis antagonist for renal proximal tubule cells. Acts through suppressing post-receptor signaling of TGF-beta1 and blocking the expression of Snail. - Chemical. CAS: 5289-74-7. Formula: C27H44O7. MW: 480.6. Isolated from Ipomoea hederacea. A member of the ecdysteroid family. Ecdysone receptor (EcR) agonist. More potent than ecdysone. Induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires, and it causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Plays a key role in insect development, cell proliferaton, growth and apoptosis by controlling gene expression involved in moulting and metamorphosis. It acts through a heterodimeric receptor comprising the ecdysone receptor and the ultraspiracle proteins (USP). Regulates lipolysis in insects. Appears in many plants mostly as a protection agent (toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. Used for controlled gene expression in scientific research, agriculture and medicine. Used for the development of selective insect growth regulators for use as environmentally benign insecticides. Shows biological effects on mammalian species. Neurosteroid. Antiepileptic. Acts on the modulatory site of the GABAA receptor and potentiates GABAergic inhibition in rat. Was shown to stimulate and modulate neutrophil production. Antidiabetic and antiobesity. Could be used as a nutritional supplement for the prevention and treatment of obesity and obesity-associated disorders. May protect PC12 cells against CoCl(2)-induced cell injury by inhibiting ROS production and modulating components of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Does not have potent anabolic properties, however, a muscle-specific increase is observed and genes are identified to provide an explanation for the muscle accretion. Potential fibrosis antagonist for renal proximal tubule cells. Acts through suppressing post-receptor signaling of TGF-beta1 and blocking the expression of Snail.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2(O)C3=CC(=O)[C@]4([H])C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C[C@]4(C)C3CC[C@]12C)[C@@](C)(O)[C@H](O)CCC(C)(C)O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Crustecdysone [5289-74-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/5D/CgoaEGayPY6EGeYaAAAAAFzNiCM674.png)
