Chemical Structure
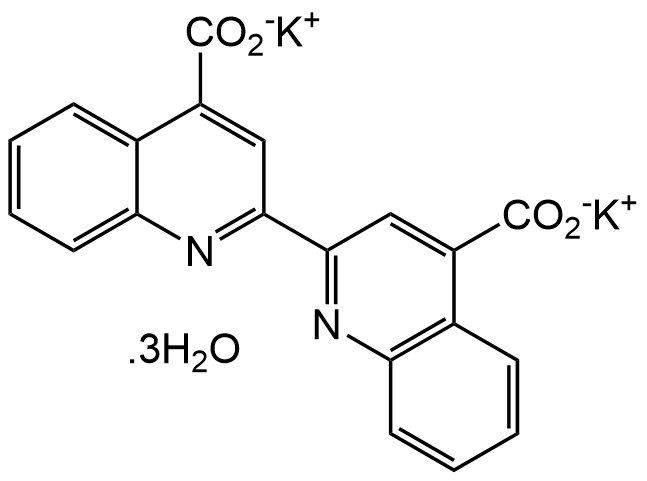
2,2-Bicinchoninic acid dipotassium salt trihydrate [207124-63-8] [207124-63-8]
CDX-B0719
CAS Number207124-63-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight474.55
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product Name2,2-Bicinchoninic acid dipotassium salt trihydrate [207124-63-8] [207124-63-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number207124-63-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC20H10K2N2O4 . 3H2O
- Molecular Weight474.55
- Scientific Description2,2-Biquinoline-4,4-dicarboxylic acid dipotassium salt (BQC) is a water soluble biquinoline-based ligand. The oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes and ketones, which can be performed by a variety of methods, remains one of the most important reactions in organic synthesis. BOC is used in the aerobic oxidation of alcohols (primary, secondary and benzylic) in the presence of palladium catalysts. The catalytic system composed of CuCl2 and BQC was found to be highly efficient for the selective oxidation of secondary benzylic, allylic and propargylic alcohols to the corresponding ketones, with aqueous t-butyl hydroperoxide under phase-transfer catalysis conditions. The catalytic system is stable and can be recycled and reused several times without loss of activity. Since the reaction solvent is only water and the oxidant is air, it may be used as a solvnt-free green alternative to the traditional methods of oxidation. BOC has also been used as an aqueous-phase catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitriles. As a complexing agent, BOC assists in the identification, extraction, and quantification of metal residues. BOC has been used for the determination of copper in wine. It binds to Cu(I) and forms a water-soluble complex that absorbs strongly at 562 nm. - Chemical. CAS: 207124-63-8. Formula: C20H10K2N2O4 . 3H2O. MW: 474.55. 2,2-Biquinoline-4,4-dicarboxylic acid dipotassium salt (BQC) is a water soluble biquinoline-based ligand. The oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes and ketones, which can be performed by a variety of methods, remains one of the most important reactions in organic synthesis. BOC is used in the aerobic oxidation of alcohols (primary, secondary and benzylic) in the presence of palladium catalysts. The catalytic system composed of CuCl2 and BQC was found to be highly efficient for the selective oxidation of secondary benzylic, allylic and propargylic alcohols to the corresponding ketones, with aqueous t-butyl hydroperoxide under phase-transfer catalysis conditions. The catalytic system is stable and can be recycled and reused several times without loss of activity. Since the reaction solvent is only water and the oxidant is air, it may be used as a solvnt-free green alternative to the traditional methods of oxidation. BOC has also been used as an aqueous-phase catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitriles. As a complexing agent, BOC assists in the identification, extraction, and quantification of metal residues. BOC has been used for the determination of copper in wine. It binds to Cu(I) and forms a water-soluble complex that absorbs strongly at 562 nm.
- SMILES[K+].[K+].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].[H]O[H].[O-]C(=O)c1cc(nc2ccccc12)-c3cc(C([O-])=O)c4ccccc4n3
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200
