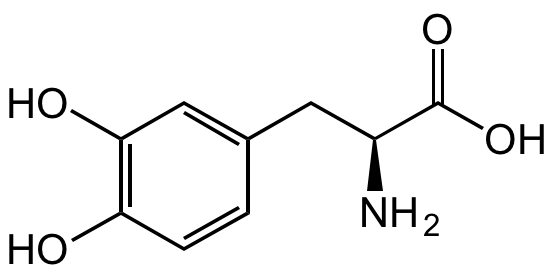
Chemical Structure
3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine [59-92-7] [59-92-7]
CDX-D0465
CAS Number59-92-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight197.19
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product Name3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine [59-92-7] [59-92-7]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number59-92-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC9H11NO4
- Molecular Weight197.19
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 59-92-7. Formula: C9H11NO4. MW: 197.19. Synthetic. Metabolic precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. This amino acid is produced from L-tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase and metabolized by catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). L-DOPA is capable of crossing the blood brain barrier where it is converted to dopamine. Formulations containing L-DOPA have been used to increase dopamine concentrations in the brain as a treatment for Parkinsons disease and stroke recovery. Mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. Used for the treatment of Parkinsons disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. In addition it is used, as a cell adhesion molecule in serum-free cultures of anchorage-dependent mammalian cells, to prevent surfaces from fouling by bonding antifouling polymers to a susceptible substrate or to stain melanocytes. - Metabolic precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. This amino acid is produced from L-tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase and metabolized by catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). L-DOPA is capable of crossing the blood brain barrier where it is converted to dopamine. Formulations containing L-DOPA have been used to increase dopamine concentrations in the brain as a treatment for Parkinsons disease and stroke recovery. Mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. Used for the treatment of Parkinsons disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. In addition it is used, as a cell adhesion molecule in serum-free cultures of anchorage-dependent mammalian cells, to prevent surfaces from fouling by bonding antifouling polymers to a susceptible substrate or to stain melanocytes.
- SMILESOC1=C(O)C=CC(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=C1
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200


![L-DOPA [59-92-7] [59-92-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/F7/CgoaEWayM0uELHzWAAAAALvoCIE466.png)
![Levodopa [59-92-7]](https://bpsbioscience.com/media/catalog/product/7/9/79792.png)
