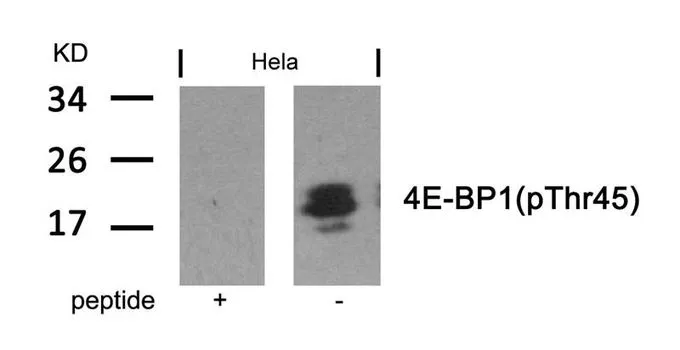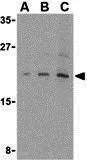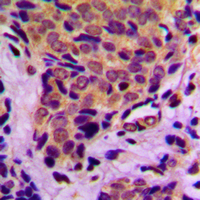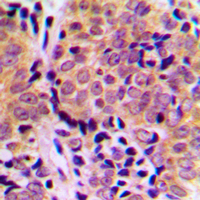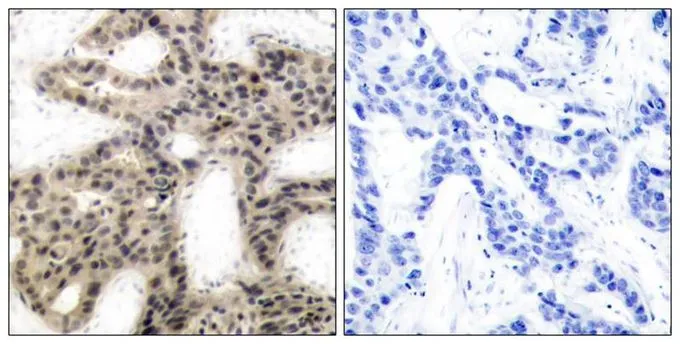
IHC-P analysis of human breast carcinoma tissue using GTX50259 4E-BP1 (phospho Thr45) antibody. Left : Primary antibody Right : Primary antibody pre-incubated with the antigen specific peptide
4E-BP1 (phospho Thr45) antibody
GTX50259
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
TargetEIF4EBP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Name4E-BP1 (phospho Thr45) antibody - Orthogonal Validated
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:50-1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1978
- Target nameEIF4EBP1
- Target descriptioneukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1
- Target synonyms4E-BP1, 4EBP1, BP-1, PHAS-I, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1, eIF4E-binding protein 1, phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein regulated by insulin 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes one member of a family of translation repressor proteins. The protein directly interacts with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), which is a limiting component of the multisubunit complex that recruits 40S ribosomal subunits to the 5 end of mRNAs. Interaction of this protein with eIF4E inhibits complex assembly and represses translation. This protein is phosphorylated in response to various signals including UV irradiation and insulin signaling, resulting in its dissociation from eIF4E and activation of mRNA translation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Cellular energy metabolism maintains young status in old queen honey bees (Apis mellifera). Lu CY et al., 2018 Aug, Arch Insect Biochem PhysiolRead more