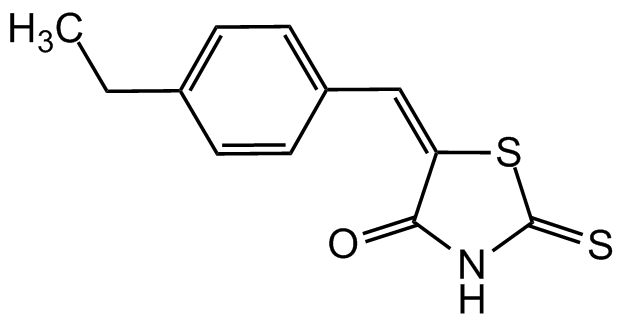
Chemical Structure
5-[(4-Ethylphenyl)methylene]-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone [403811-55-2] [403811-55-2]
CDX-E0533
CAS Number403811-55-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight249.35
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product Name5-[(4-Ethylphenyl)methylene]-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone [403811-55-2] [403811-55-2]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number403811-55-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC12H11NOS2
- Molecular Weight249.35
- Scientific Descriptionc-Myc is a proto-oncogene that plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. 5-[(4-Ethylphenyl)methylene]-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone [10058-F4] is a cell-permeable thiazolidinone compound that specifically inhibits the c-Myc-Max interaction/dimerization at 64 microM, preventing c-Myc-dependent gene expression and cell proliferation. 10058-F4 inhibits tumor cell growth and proliferation in a c-Myc-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo. 10058-F4 induces cell-cycle arrest (G0/G1 phase) and apoptosis. 10058-F4 has been found to also upregulate cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors, p21 and p27. In addition to c-Myc, 10058-F4 inhibits the nuclear Myc protein, N-Myc, at 50 microM, inducing arrest, apoptosis, and differentiation in neuroblastoma cells overexpressing the gene for N-Myc. This compound can be used to delineate novel actions of Myc proteins, especially those related to lipid and glucose metabolism. 10058-F4 downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase and enhances chemosensitivity in several human cancer cell lines. - Chemical. CAS: 403811-55-2. Formula: C12H11NOS2. MW: 249.35. c-Myc is a proto-oncogene that plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. 5-[(4-Ethylphenyl)methylene]-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone [10058-F4] is a cell-permeable thiazolidinone compound that specifically inhibits the c-Myc-Max interaction/dimerization at 64 microM, preventing c-Myc-dependent gene expression and cell proliferation. 10058-F4 inhibits tumor cell growth and proliferation in a c-Myc-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo. 10058-F4 induces cell-cycle arrest (G0/G1 phase) and apoptosis. 10058-F4 has been found to also upregulate cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors, p21 and p27. In addition to c-Myc, 10058-F4 inhibits the nuclear Myc protein, N-Myc, at 50 microM, inducing arrest, apoptosis, and differentiation in neuroblastoma cells overexpressing the gene for N-Myc. This compound can be used to delineate novel actions of Myc proteins, especially those related to lipid and glucose metabolism. 10058-F4 downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase and enhances chemosensitivity in several human cancer cell lines.
- SMILESO=C(NC(S/1)=S)C1=C/C2=CC=C(CC)C=C2
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200


![10058-F4 [403811-55-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/B9/CgoaEWayQviEUM2-AAAAAIV8xxQ950.png)