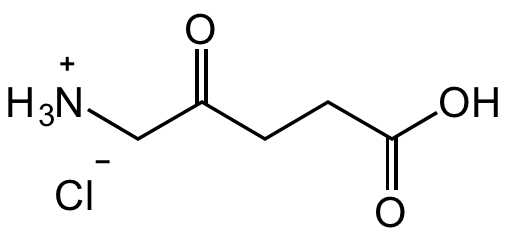
Chemical Structure
5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride [5451-09-2]
CDX-A0364
CAS Number5451-09-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight131.13 . 36.46
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product Name5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride [5451-09-2]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number5451-09-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC5H9NO3 . HCl
- Molecular Weight131.13 . 36.46
- Scientific Description5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) is a non-proteinogenic five carbon amino acid, which is the precursor for the biosynthesis of tetrapyrrole compounds, such as heme, chlorophyll and vitamin B12 and has broad applications in the medical and agricultural fields. The conversion of 5-ALA to protoporphyrins within tissues produces a photosensitive target that produces reactive oxygen species upon exposure to light. In this way, it is used in photodynamic therapy for a range of dermatological conditions, cancers, and other diseases. Oral administration of 5-ALA leads to the preferential accumulation of the fluorescent molecule protoporphyrin IX within certain types of cancer cells. This allows fluorescence-based identification of tumor tissue for accurate resection of diseased tissue. In addition to tumor therapy, 5-ALA has been implicated in the treatment of inflammatory disease, autoimmune disease and transplantation due to the anti-inflammation and immunoregulation properties that are elicited with the expression of heme oxygenase (HO)-1. ALA-based photodynamic therapy (PDT) has also a role in the treatment of microbial infections. - Chemical. CAS: 5451-09-2. Formula: C5H9NO3 . HCl. MW: 131.13 . 36.46. 5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) is a non-proteinogenic five carbon amino acid, which is the precursor for the biosynthesis of tetrapyrrole compounds, such as heme, chlorophyll and vitamin B12 and has broad applications in the medical and agricultural fields. The conversion of 5-ALA to protoporphyrins within tissues produces a photosensitive target that produces reactive oxygen species upon exposure to light. In this way, it is used in photodynamic therapy for a range of dermatological conditions, cancers, and other diseases. Oral administration of 5-ALA leads to the preferential accumulation of the fluorescent molecule protoporphyrin IX within certain types of cancer cells. This allows fluorescence-based identification of tumor tissue for accurate resection of diseased tissue. In addition to tumor therapy, 5-ALA has been implicated in the treatment of inflammatory disease, autoimmune disease and transplantation due to the anti-inflammation and immunoregulation properties that are elicited with the expression of heme oxygenase (HO)-1. ALA-based photodynamic therapy (PDT) has also a role in the treatment of microbial infections.
- SMILES[NH3+]CC(CCC(O)=O)=O.[Cl-]
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride [5451-09-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/52/CgoaEGY7L8CEWE42AAAAAAO_lHU966.png)