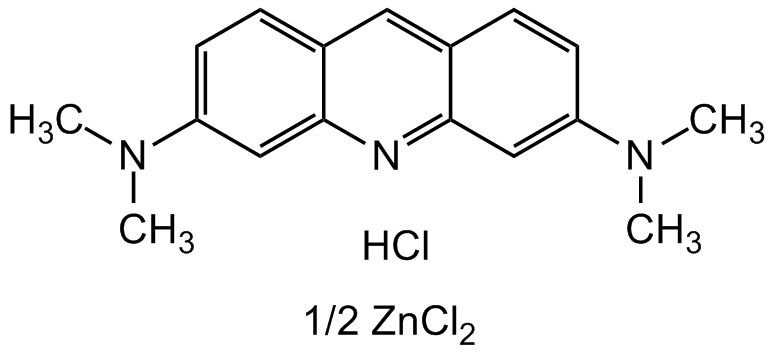
Chemical Structure
Acridine Orange hemi(zinc chloride) salt [10127-02-3] [10127-02-3]
CDX-A0668
CAS Number10127-02-3
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>90%
Molecular Weight369.96
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameAcridine Orange hemi(zinc chloride) salt [10127-02-3] [10127-02-3]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number10127-02-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC17H20ClN3 . HCl . 1/2ZnCl2
- Molecular Weight369.96
- Scientific DescriptionAcridine Orange hemi(zinc chloride) salt is a cell-permeable metachromatic fluorescent dye that stains DNA and RNA. It is used as a nucleic acid-selective fluorescent cationic dye useful for cell cycle determination. Being cell-permeable, it interacts with DNA and RNA by intercalation or electrostatic attractions respectively. When bound to DNA, it is very similar spectrally to fluorescein, with an excitation maximum at 502nm and an emission maximum at 525nm (green). When acridine orange associates with RNA, the excitation maximum shifts to 460nm (blue), and the emission maximum shifts to 650nm (red). Acridine orange will also enter acidic compartments such as lysosomes where it becomes protonated and sequestered. Within these low pH vesicles, the dye emits red fluorescence when excited by blue light. Thus, acridine orange can be used to visualize primary lysosomes and phagolysosomes that may include products of phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. The dye is often used in epifluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry.It allows for visual detection of nucleic acids on agarose and polyacrylamide gels, can be used for differentiation of dsDNA (green fluorescence) and ssDNA/RNA (orange fluorescence) and as a vitality test for determination of living cells. Spectral data: lambdaEx=502nm, lambdaEm=525nm (green, double strands) / lambdaEx=460nm, lambdaEm=650nm (red, single strands). - Chemical. CAS: 10127-02-3. Formula: C17H20ClN3 . HCl . 1/2ZnCl2. MW: 369.96. Acridine Orange hemi(zinc chloride) salt is a cell-permeable metachromatic fluorescent dye that stains DNA and RNA. It is used as a nucleic acid-selective fluorescent cationic dye useful for cell cycle determination. Being cell-permeable, it interacts with DNA and RNA by intercalation or electrostatic attractions respectively. When bound to DNA, it is very similar spectrally to fluorescein, with an excitation maximum at 502nm and an emission maximum at 525nm (green). When acridine orange associates with RNA, the excitation maximum shifts to 460nm (blue), and the emission maximum shifts to 650nm (red). Acridine orange will also enter acidic compartments such as lysosomes where it becomes protonated and sequestered. Within these low pH vesicles, the dye emits red fluorescence when excited by blue light. Thus, acridine orange can be used to visualize primary lysosomes and phagolysosomes that may include products of phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. The dye is often used in epifluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry.It allows for visual detection of nucleic acids on agarose and polyacrylamide gels, can be used for differentiation of dsDNA (green fluorescence) and ssDNA/RNA (orange fluorescence) and as a vitality test for determination of living cells. Spectral data: lambdaEx=502nm, lambdaEm=525nm (green, double strands) / lambdaEx=460nm, lambdaEm=650nm (red, single strands).
- SMILESCl[Zn]Cl.CN(C)C1=CC=C2C(N=C(C=C(N(C)C)C=C3)C3=C2)=C1.Cl
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12162000

![Euchrysine 3RX [10127-02-3] [10127-02-3]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/86/CgoaEWY7MEKEDHl-AAAAADLL6pA796.png)