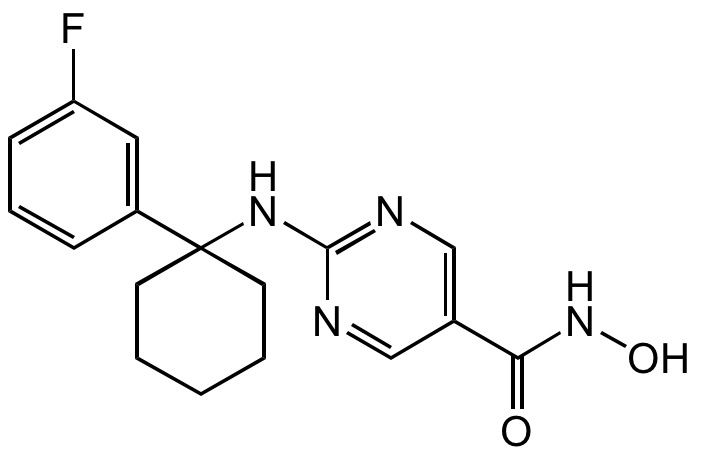
Chemical Structure
ACY-775
AG-CR1-3903
CAS Number1375466-18-4
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight330.4
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameACY-775
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number1375466-18-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC17H19FN4O2
- Molecular Weight330.4
- Scientific DescriptionCell permeable, potent and selective class IIb HDAC6 inhibitor (IC50 =7.5nM). Displays high selectivity over HDAC1-9 (IC50=1-10microM). Shows improved brain bioavailability compared to tubastatin A (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3900). Induces hyperacetylation of alpha-tubulin in brain without concurrently altering the acetylation of histones. Shows antidepressant activity. HDAC6 deacetylates tubulin, HSP90 and the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, H4). Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. HDAC6 plays an important role in microtubule-dependent cell motility, transcriptional regulation, degradation of misfolded proteins and cell cycle and is involved in autophagy, inflammation, cancer and neurodegeneration. - Chemical. CAS: 1375466-18-4. Formula: C17H19FN4O2. MW: 330.4. Cell permeable, potent and selective class IIb HDAC6 inhibitor (IC50 =7.5nM). Displays high selectivity over HDAC1-9 (IC50=1-10microM). Shows improved brain bioavailability compared to tubastatin A (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3900). Induces hyperacetylation of alpha-tubulin in brain without concurrently altering the acetylation of histones. Shows antidepressant activity. HDAC6 deacetylates tubulin, HSP90 and the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, H4). Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. HDAC6 plays an important role in microtubule-dependent cell motility, transcriptional regulation, degradation of misfolded proteins and cell cycle and is involved in autophagy, inflammation, cancer and neurodegeneration.
- SMILESONC(=O)C1=CN=C(NC2(CCCCC2)C2=CC(F)=CC=C2)N=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![ACY-775 [1375466-18-4]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/F8/CgoaEWayM16EWOJCAAAAAHEHl0I437.png)
