Products
Are you looking for life science and diagnostic reagents? We offer one of the most extensive ranges in the Benelux. There are currently more than 8 million products in our webshop, which are manufactured by more than 130 suppliers. We hope to support your research with everything you need.
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDQ04206
- SizePrice
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP19838
- SizePrice
Product group Assays
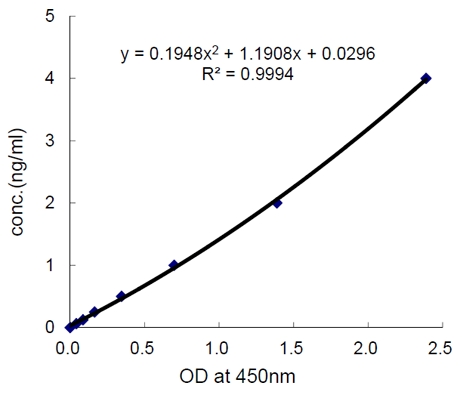
Irisin Competitive ELISA KitAG-45A-0046YEK
ReactivityHuman, Monkey, Mouse, Rat
- SizePrice
Product group Chemicals
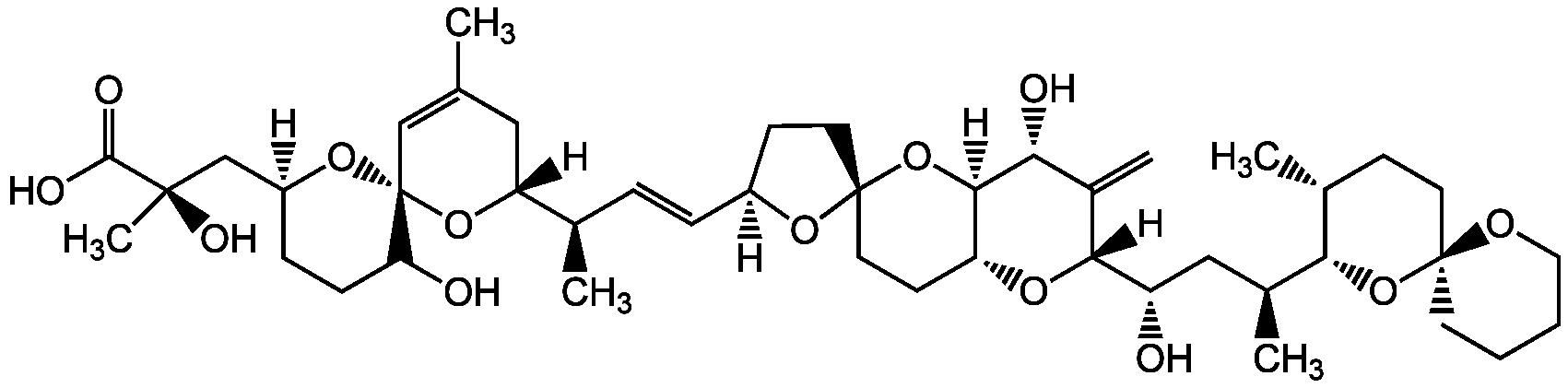
Okadaic acid (high purity)AG-CN2-0056
CAS Number78111-17-8
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight805
- SizePrice
Product group Chemicals
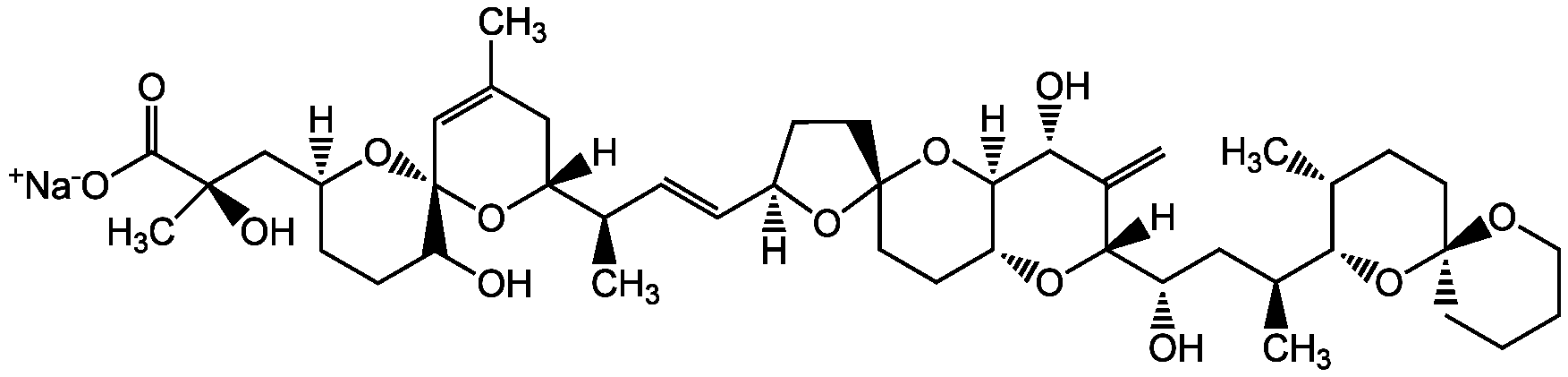
Okadaic acid . sodium salt (high purity)AG-CN2-0062
CAS Number209266-80-8
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight804.0 . 23.0
- SizePrice
Product group Chemicals
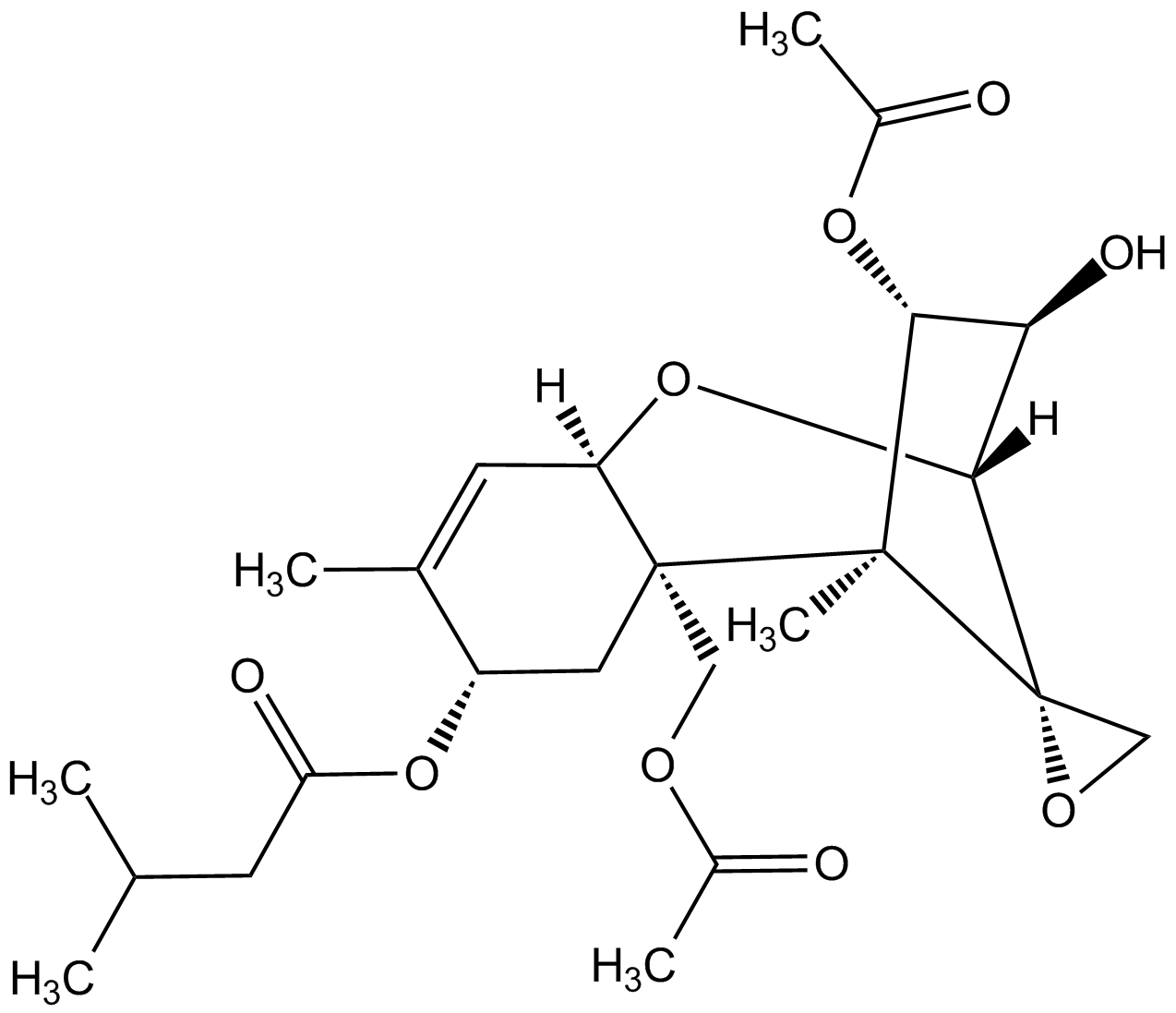
T-2 ToxinAG-CN2-0473
CAS Number21259-20-1
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight466.5
- SizePrice
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Search through our product groups to find the right product
Back to overview