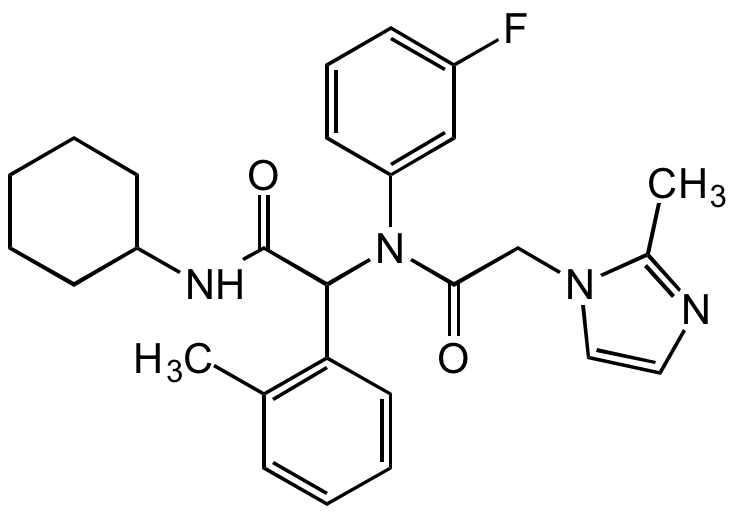
Chemical Structure
AGI-5198 [1355326-35-0] [1355326-35-0]
AG-CR1-3528
CAS Number1355326-35-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight462.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAGI-5198 [1355326-35-0] [1355326-35-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number1355326-35-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC27H31FN4O2
- Molecular Weight462.6
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 1355326-35-0. Formula: C27H31FN4O2. MW: 462.6. Synthetic. Potent and selective inhibitor of IDH1 (isocitrate dehydrogenase 1) R132H and R132C mutants in vitro with IC50 values of 0.07 and 0.16 microM, respectively. Does not inhibit wild-type IDH1 or any of the examined IDH2 isoforms (IC50 > 100 microM). Isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDHs) are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and NAD phosphate (NADP+)-dependent enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle that catalyze oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate producing alpha-ketoglutarate (2-OG) and carbon dioxide. IDH1 and IDH2 are mutated in >70% of lower grade gliomas. Shown to have anti-tumor efficacy in the TS603 glioma cell line and to reduce tumor 2-HG production in HT1080 and U87MG cells. Caused 50-60% growth inhibition over a treatment period of three weeks with no affect in the growth of IDH1 wild-type glioma xenografts in R132H-IDH1 glioma xenografts. Under conditions of near complete 2-HG inhibition, induces demethylation of histone H3K9me3 and expression of genes associated with gliogenic differentiation. Useful chemical probe to assess the biological consequences of IDH1 mutations and the potential of IDH1 inhibiton for treating IDH1 mutant tumors. Requires high doses for in vivo activity, but can be used through oral dosing route. - Potent and selective inhibitor of IDH1 (isocitrate dehydrogenase 1) R132H and R132C mutants in vitro with IC50 values of 0.07 and 0.16microM, respectively. Does not inhibit wild-type IDH1 or any of the examined IDH2 isoforms (IC50>100microM). Isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDHs) are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and NAD phosphate (NADP+)-dependent enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle that catalyze oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate producing alpha-ketoglutarate (2-OG) and carbon dioxide. IDH1 and IDH2 are mutated in >70% of lower grade gliomas. Shown to have anti-tumor efficacy in the TS603 glioma cell line and to reduce tumor 2-HG production in HT1080 and U87MG cells. Caused 50-60% growth inhibition over a treatment period of three weeks with no affect in the growth of IDH1 wild-type glioma xenografts in R132H-IDH1 glioma xenografts. Under conditions of near complete 2-HG inhibition, induces demethylation of histone H3K9me3 and expression of genes associated with gliogenic differentiation. Useful chemical probe to assess the biological consequences of IDH1 mutations and the potential of IDH1 inhibition for treating IDH1 mutant tumors. Requires high doses for in vivo activity, but can be used through oral dosing route.
- SMILESO=C(C(C1=C(C)C=CC=C1)N(C2=CC(F)=CC=C2)C(CN3C=CN=C3C)=O)NC4CCCCC4
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN2811
- UNSPSC12352200

![AGI-5198 [1355326-35-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/8A/CgoaEGayQCSESgIqAAAAAEN0RnA855.png)
