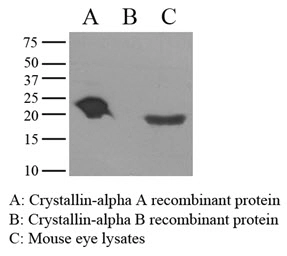
Mouse eye extracts and recombinant proteins (Crystallin-alpha A and B) were resolved by electrophoresis, transferred to PVDF membrane and probed with anti-Crystallin alpha A (1:1000). Proteins were visualized using a goat anti-mouse secondary antibody con
alpha A Crystallin antibody [c9F2]
GTX50077
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCRYAA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namealpha A Crystallin antibody [c9F2]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWe recommend the following starting dilutions:Western blot analysis: 1:500 ~ 1:2000. Optimal working concentrations should be determined experimentally by the end user.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDc9F2
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1409
- Target nameCRYAA
- Target descriptioncrystallin alpha A
- Target synonymsCRYA1, CTRCT9, HSPB4, alpha-crystallin A chain, crystallin, alpha-1, heat shock protein beta-4, heat shock protein family B member 4, human alphaA-crystallin (CRYA1)
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDA0A140G945
- Protein NameAlpha-crystallin A chain
- Scientific DescriptionMammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families. Alpha crystallins are composed of two gene products: alpha-A and alpha-B, for acidic and basic, respectively. Alpha crystallins can be induced by heat shock and are members of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family. They act as molecular chaperones although they do not renature proteins and release them in the fashion of a true chaperone; instead they hold them in large soluble aggregates. Post-translational modifications decrease the ability to chaperone. These heterogeneous aggregates consist of 30-40 subunits; the alpha-A and alpha-B subunits have a 3:1 ratio, respectively. Two additional functions of alpha crystallins are an autokinase activity and participation in the intracellular architecture. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Alpha-A and alpha-B gene products are differentially expressed; alpha-A is preferentially restricted to the lens and alpha-B is expressed widely in many tissues and organs. Defects in this gene cause autosomal dominant congenital cataract (ADCC). [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

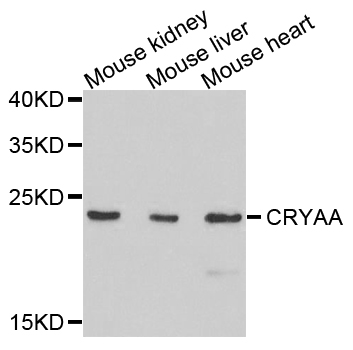




![WB analysis of various samples using GTX03188 alpha A Crystallin antibody [GT1276]. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX03188/GTX03188_40_WB_w_23053123_171.webp)