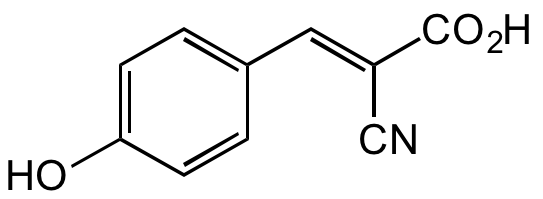
Chemical Structure
alpha-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid [28166-41-8]

AG-CR1-3686
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Namealpha-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid [28166-41-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number28166-41-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC10H7NO3
- Molecular Weight189.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 28166-41-8. Formula: C10H7NO3. MW: 189.2. . Specific monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) inhibitor. Inhibits mitochondrial lactate and pyruvate transport. Decreases glycolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Exhibits antitumoral and antiangiogenic activity in gliomas in vivo; decreases glycolytic metabolism, migration and invasion. Blocks lactate efflux from glioma cells and sensitizes cells to irradiation. Highly malignant tumors rely heavily on aerobic glycolysis (metabolism of glucose to lactic acid even under presence of oxygen; Warburg Effect) and thus need to efflux lactic acid via MCTs to the tumor micro-environment to maintain a robust glycolytic flux and to prevent the tumor from apoptosis. Inhibiting lactic acid efflux is a very effective therapeutic strategy against highly glycolytic malignant tumors. Common organic matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) matrix. - Specific monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) inhibitor. Inhibits mitochondrial lactate and pyruvate transport. Decreases glycolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Exhibits antitumoral and antiangiogenic activity in gliomas in vivo; decreases glycolytic metabolism, migration and invasion. Blocks lactate efflux from glioma cells and sensitizes cells to irradiation. Highly malignant tumors rely heavily on aerobic glycolysis (metabolism of glucose to lactic acid even under presence of oxygen; Warburg Effect) and thus need to efflux lactic acid via MCTs to the tumor micro-environment to maintain a robust glycolytic flux and to prevent the tumor from apoptosis. Inhibiting lactic acid efflux is a very effective therapeutic strategy against highly glycolytic malignant tumors. Common organic matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) matrix.
- SMILESOC1=CC=C(/C=C(C#N)/C(O)=O)C=C1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Role of mitochondrial lactate dehydrogenase and lactate oxidation in the intracellular lactate shuttle: G.A. Brooks, et al.; PNAS 96, 1129 (1999)
- Pyruvate fuels mitochondrial respiration and proliferation of breast cancer cells: effect of monocarboxylate transporter inhibition: A.R. Diers, et al.; Biochem. J. 444, 561 (2012)
- The monocarboxylate transporter inhibitor alpha-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid disrupts rat lung branching: S. Granja, et al.; Cell Physiol. Biochem. 32, 1845 (2013)
- A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016)
- Similarities and Distinctions of Cancer and Immune Metabolism in Inflammation and Tumors: G. Andrejeva & J.C. Rathmell; Cell Metab. 26, 49 (2017)
- Metabolic Instruction of Immunity: M.D. Buck, et al.; Cell 169, 570 (2017)
