Chemical Structure
Anacardic acid [16611-84-0]

AG-CR1-0046
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAnacardic acid [16611-84-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number16611-84-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
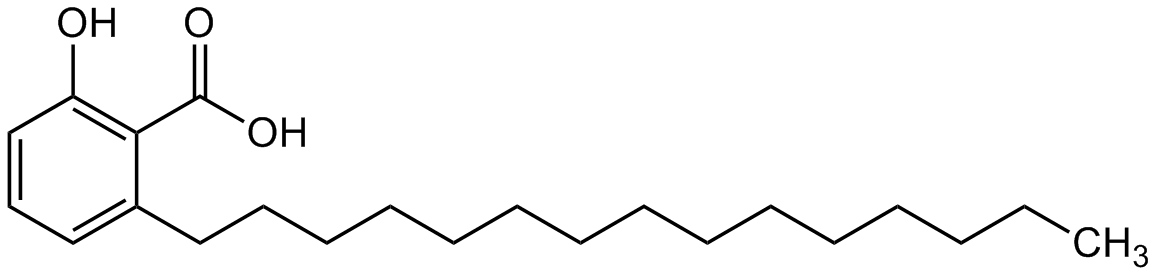
- Molecular FormulaC22H36O3
- Molecular Weight348.5
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 16611-84-0. Formula: C22H36O3. MW: 348.5. Potent histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitor. Antibacterial. SUMOylation inhibitor. Lipoxygenase inhibitor. NF-kappaB inhibitor. Anti-tumor compound. Anti-inflammatory. Apoptosis inducer. Antiproliferative. - Potent histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitor [1, 2]. Antibacterial [3]. SUMOylation inhibitor [4]. Lipoxygenase inhibitor [5]. NF-kappaB inhibitor [6]. Anti-tumor compound [2, 6-8]. Anti-inflammatory [6]. Apoptosis inducer [6, 7]. Antiproliferative [7].
- SMILESCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC(O)=C1C(O)=O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Small molecule modulators of histone acetyltransferase p300: K. Balasubramanyam, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 278, 19134 (2003)
- Inhibition of histone acetyltransferase activity by anacardic acid sensitizes tumor cells to ionizing radiation: Y. Sun, et al.; FEBS Lett. 580, 4353 (2006)
- Antibacterial activity of anacardic acid and totarol, alone and in combination with methicillin, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: H. Muroi & I. Kubo; J. Appl. Bacteriol. 80, 387 (1996)
- Ginkgolic acid inhibits protein SUMOylation by blocking formation of the E1-SUMO intermediate: I. Fukuda, et al.; Chem. Biol. 16, 133 (2009)
- Inhibition of lipoxygenase and prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase by anacardic acids: R. Grazzini, et al.; BBRC 176, 775 (1991)
- Anacardic acid (6-nonadecyl salicylic acid), an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase, suppresses expression of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products involved in cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and inflammation through inhibition of the inhibitory subunit of nuclear factor-kappaBalpha kinase, leading to potentiation of apoptosis: B. Sung, et al.; Blood 111, 4880 (2008)
- Anacardic acid induces caspase-independent apoptosis and radiosensitizes pituitary adenoma cells: S. Sukumari-Ramesh, et al.; J. Neurosurg. 114, 1681 (2011)
- Anacardic acid inhibits estrogen receptor alpha-DNA binding and reduces target gene transcription and breast cancer cell proliferation: D.J. Schultz, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 9, 594 (2010)
