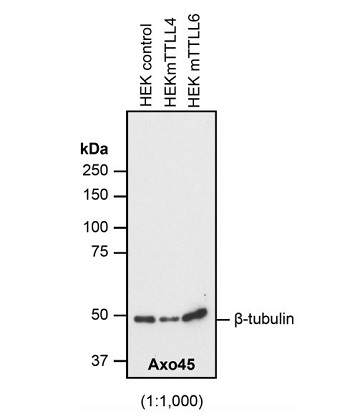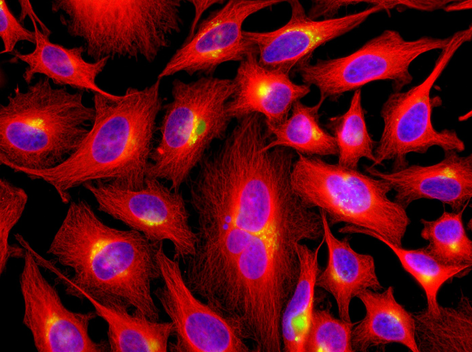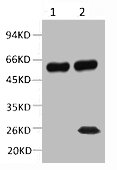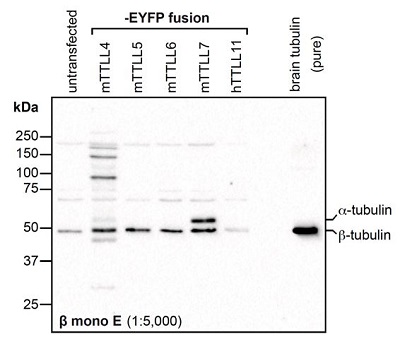
Figure 1: Immunoblot analysis of protein glutamylation with anti-beta-Tubulin (beta-monoE), pAb (IN115) (Prod. No. AG-25B-0039). Method: HEK-293T cells are grown in standard culture conditions, transfected with plasmids expressing the different glutamylases and are run on a 10% SDS-PAGE (specific protocol to separate alpha- and beta-tubulin (Magiera & Janke, 2013)). Tubulin purified from pork brain was used as a positive control for glutamylated tubulin. The proteins are transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and detected by standard immunoblot protocol using the beta-monoE (1:5,000) in PBS containing 0.1% Tween-20 for washing steps and 2.5% fat free milk for antibody incubation. In untransfected HEK-293T cell extracts, no tubulin is detected, even on high exposure. After expression of TTLL4, predominantly beta-tubulin is detected with beta-monoE, but the antibody also faintly detects the heterogeneous mixture of different, yet unidentified substrates modified by TTLL4. In cells expressing TTLL5 and TTLL6, the beta-monoE detects only beta-tubulin, while expression of TTLL7 generates beta-monoE-positive alpha- and beta-tubulin. In the purified brain tubulin, the antibody specifically detects glutamylation of beta-tubulin. Picture courtesy of Sudarshan Gadadhar, Shreyangi Chakraborty, Mariya Genova and Carsten Janke, Institut Curie, Orsay.
anti-beta-Tubulin (beta-monoE), pAb (IN115)
AG-25B-0039
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetTUBB2A
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-beta-Tubulin (beta-monoE), pAb (IN115)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID7280
- Target nameTUBB2A
- Target descriptiontubulin beta 2A class IIa
- Target synonymsCDCBM5, TUBB, TUBB2, tubulin beta-2A chain, class IIa beta-tubulin, tubulin, beta 2A, tubulin, beta polypeptide 2
- HostRabbit
- Protein IDQ13885
- Protein NameTubulin beta-2A chain
- Scientific DescriptionPolyclonal Antibody. Recognizes the posttranslational modification glutamylation with specific reactivity for the GE(*-E)F motive. Because the sequence GEF is specific to several beta-tubulin isotypes, the antibody selectively detects mono-glutamylated beta-tubulin. Applications: ICC, IHC, IP, WB. Source: Rabbit. Polyglutamylation is an evolutionarily conserved protein post-translational modification in which glutamate side chains of variable lengths are formed on the modified protein. The most prominent substrate is tubulin, the building block of microtubules (MTs). Polyglutamylation has been found on both, alpha- and beta-tubulin. It is catalyzed by multiple enzymes that belong to the family of tubulin tyrosine-ligase like (TTLL) enzymes. These TTLLs have substrate (alpha- vs beta-tubulin) as well as reaction (initiation vs elongation) specificities. These subtle changes in levels of polyglutamylation on specific tubulin isoforms could in turn be influencing the diverse MT functions that are regulated by polyglutamylation. The beta-monoE antibody selectively labels glutamylation of beta-tubulin due to its specificity to a sequence motif (GE(*-E)F) that only exists in beta-tubulin isotypes. It allows to specifically detect beta-tubulin glutamylation in brain tubulin, where other antibodies predominantly detect alpha-tubulin glutamylation. - Polyglutamylation is an evolutionarily conserved protein post-translational modification in which glutamate side chains of variable lengths are formed on the modified protein. The most prominent substrate is tubulin, the building block of microtubules (MTs). Polyglutamylation has been found on both, alpha- and beta-tubulin. It is catalyzed by multiple enzymes that belong to the family of tubulin tyrosine-ligase like (TTLL) enzymes. These TTLLs have substrate (alpha- vs beta-tubulin) as well as reaction (initiation vs elongation) specificities. These subtle changes in levels of polyglutamylation on specific tubulin isoforms could in turn be influencing the diverse MT functions that are regulated by polyglutamylation. The beta-monoE antibody selectively labels glutamylation of beta-tubulin due to its specificity to a sequence motif (GE(*-E)F) that only exists in beta-tubulin isotypes. It allows to specifically detect beta-tubulin glutamylation in brain tubulin, where other antibodies predominantly detect alpha-tubulin glutamylation.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161