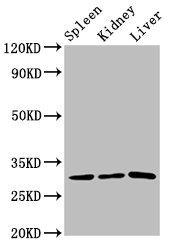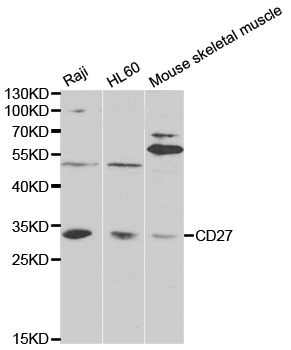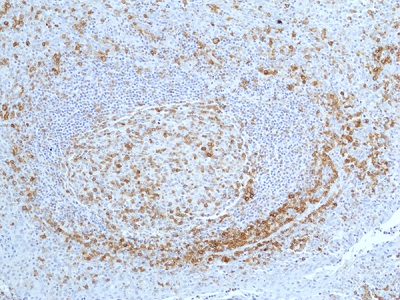
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue, using anti-CD27 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (RM501) at 1:100 dilution.
anti-CD27 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM501)
REV-31-1393-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD27
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD27 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM501)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM501
- Gene ID939
- Target nameCD27
- Target descriptionCD27 molecule
- Target synonymsS152, S152. LPFS2, T14, TNFRSF7, Tp55, CD27 antigen, CD27L receptor, T cell activation antigen S152, T-cell activation antigen CD27, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 7
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP26842
- Protein NameCD27 antigen
- Scientific DescriptionCD27 (TNFRSF7) is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily limited to cells of the lymphoid lineage and exists as both a dimeric glycoprotein on the cell surface and as a soluble protein in serum. As a T and B cell co-stimulatory molecule, the activity of CD27 is governed by its TNF-like ligand CD70 on lymphocytes and dendritic cells. The CD27-CD70 interaction is required for Th1 generation responses to differentiation signals and long-term maintenance of T cell immunity, and meanwhile, plays a key role in regulating B cell differentiation, activation and immunoglobulin synthesis. The CD27 receptor transduces signals and subsequently leads to the activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK8/JNK, mediated by the adaptor proteins TRAF2 and TRAF5. In addition, the proapoptotic protein SIVA is capable of binding the cytoplasmic tail of CD27 and exerts action in the process of apoptosis. The expression of CD27 and its ligand CD70 is predominantly confined to lymphocytes. High expression levels of CD27 appear to be dependent on proper ligation of antigen receptors. CD70 expression requires additional co-stimulatory and/or pro-inflammatory signals. CD27 is expressed as a disulfide-linked homodimer on mature thymocytes, peripheral blood T cells and a subpopulation of B cells. The immune checkpoint molecule CD70 and its receptor CD27 are aberrantly expressed in many hematological and solid malignancies. Dysregulation of the CD70-CD27 axis within the tumor and its microenvironment is associated with tumor progression and immunosuppression. - Recombinant Antibody. RM501 reacts to human CD27 (TNFRSF7). Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A peptide corresponding to residues near the C-terminus of human CD27. Application: IHC, WB. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD27 (TNFRSF7) is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily limited to cells of the lymphoid lineage and exists as both a dimeric glycoprotein on the cell surface and as a soluble protein in serum. As a T and B cell co-stimulatory molecule, the activity of CD27 is governed by its TNF-like ligand CD70 on lymphocytes and dendritic cells. The CD27-CD70 interaction is required for Th1 generation responses to differentiation signals and long-term maintenance of T cell immunity, and meanwhile, plays a key role in regulating B cell differentiation, activation and immunoglobulin synthesis. The CD27 receptor transduces signals and subsequently leads to the activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK8/JNK, mediated by the adaptor proteins TRAF2 and TRAF5. In addition, the proapoptotic protein SIVA is capable of binding the cytoplasmic tail of CD27 and exerts action in the process of apoptosis. The expression of CD27 and its ligand CD70 is predominantly confined to lymphocytes. High expression levels of CD27 appear to be dependent on proper ligation of antigen receptors. CD70 expression requires additional co-stimulatory and/or pro-inflammatory signals. CD27 is expressed as a disulfide-linked homodimer on mature thymocytes, peripheral blood T cells and a subpopulation of B cells. The immune checkpoint molecule CD70 and its receptor CD27 are aberrantly expressed in many hematological and solid malignancies. Dysregulation of the CD70-CD27 axis within the tumor and its microenvironment is associated with tumor progression and immunosuppression.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161