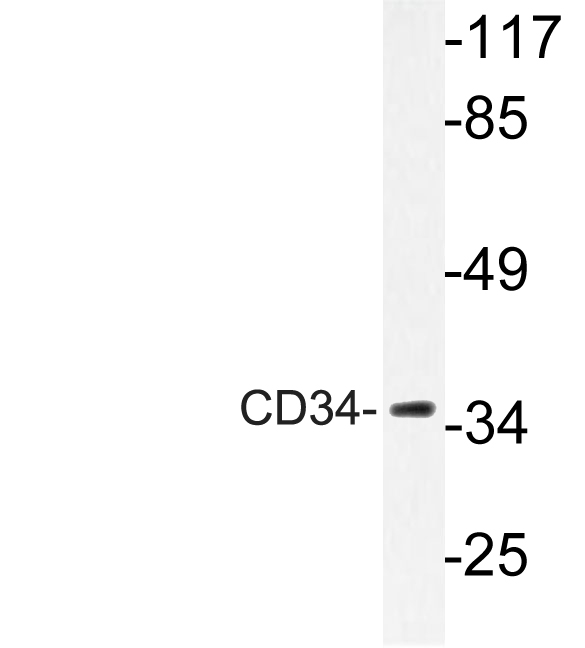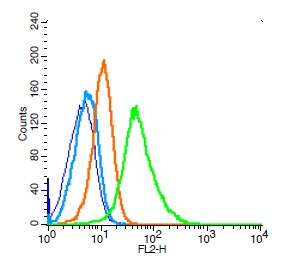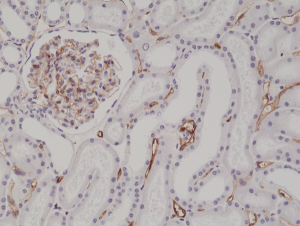
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human kidney tissue section using anti-CD34 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM300) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-CD34 (C-term), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM300)
REV-31-1185-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCD34
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD34 (C-term), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM300)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM300
- Gene ID947
- Target nameCD34
- Target descriptionCD34 molecule
- Target synonymshematopoietic progenitor cell antigen CD34, CD34 antigen, CD34 sialomucin
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP28906
- Protein NameHematopoietic progenitor cell antigen CD34
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human, mouse and rat CD34. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The CD34 family of cell surface transmembrane proteins includes the hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen CD34, Podocalyxin and Endoglycan. The single-pass sialomucin-like transmembrane protein CD34 is heavily glycosylated and phosphorylated by Protein kinase C (PKC). CD34 is a highly glycosylated monomeric surface protein that is present on many stem cell populations. CD34 is a 115 kDa glycoprotein found on multipotent precursors, bone marrow stromal cells, embryonic fibroblasts, vascular endothelia, as well as some populations of mesenchymal stem cells, and tumor cell lines. CD34 may serve as a surface receptor that undergoes receptor-mediated endocytosis and regulates adhesion, differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells and other progenitors. CD34 is possibly an adhesion molecule with a putative role for mediating the attachment of stem cells to the bone marrow extracellular matrix or directly to stromal cells. Further, CD34 could act as a scaffold for the attachment of lineage specific glycans, allowing stem cells to bind to lectins expressed by stromal cells or other marrow components. CD34 is thought to have a role in presenting carbohydrate ligands to selectins. Diseases associated with CD34 dysfunction include dermatofibrosarcoma and neurofibroma. - The CD34 family of cell surface transmembrane proteins includes the hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen CD34, Podocalyxin and Endoglycan. The single-pass sialomucin-like transmembrane protein CD34 is heavily glycosylated and phosphorylated by Protein kinase C (PKC). CD34 is a highly glycosylated monomeric surface protein that is present on many stem cell populations. CD34 is a 115 kDa glycoprotein found on multipotent precursors, bone marrow stromal cells, embryonic fibroblasts, vascular endothelia, as well as some populations of mesenchymal stem cells, and tumor cell lines. CD34 may serve as a surface receptor that undergoes receptor-mediated endocytosis and regulates adhesion, differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells and other progenitors. CD34 is possibly an adhesion molecule with a putative role for mediating the attachment of stem cells to the bone marrow extracellular matrix or directly to stromal cells. Further, CD34 could act as a scaffold for the attachment of lineage specific glycans, allowing stem cells to bind to lectins expressed by stromal cells or other marrow components. CD34 is thought to have a role in presenting carbohydrate ligands to selectins. Diseases associated with CD34 dysfunction include dermatofibrosarcoma and neurofibroma.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161