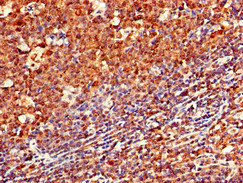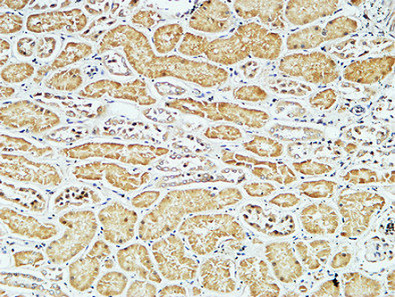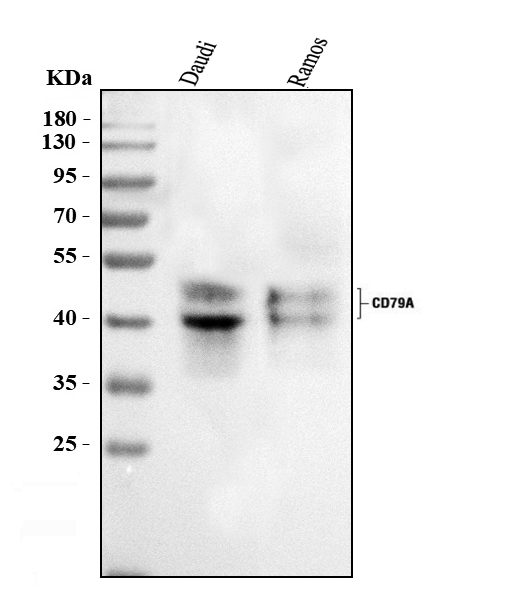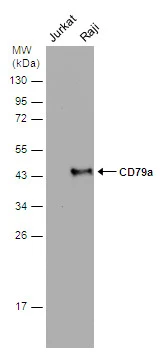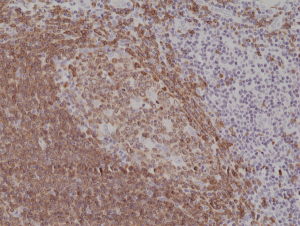
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human tonsil tissue section using anti-CD79a rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM297) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-CD79a (C-term) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM297)
REV-31-1182-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD79A
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD79a (C-term) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM297)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM297
- Gene ID973
- Target nameCD79A
- Target descriptionCD79a molecule
- Target synonymsIGA, IGAlpha, MB-1, MB1, B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain, CD79a antigen (immunoglobulin-associated alpha), CD79a molecule, immunoglobulin-associated alpha, MB-1 membrane glycoprotein, ig-alpha, membrane-bound immunoglobulin-associated protein, surface IgM-associated protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP11912
- Protein NameB-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain
- Scientific DescriptionCD79a is a disulphide-linked heterodimer together with CD79b. CD79a plays multiple and diverse roles in B cell development and function. The CD79a/b heterodimer associates non-covalently with the immunoglobulin heavy chain through its transmembrane region, thus forming the BCR along with the immunoglobulin light chain and the pre-BCR when associated with the surrogate light chain in developing B cells. Association of the CD79a/b heterodimer with the immunoglobulin heavy chain is required for surface expression of the BCR and BCR induced calcium flux and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. The CD79a protein is present on the surface of B-cells throughout their life cycle, and is absent on all other healthy cells, making it a highly reliable marker for B-cells in immunohistochemistry. The protein remains present when B cells transform into active plasma cells, and is also present in virtually all B-cell neoplasms, including B-cell lymphomas, plasmacytomas and myelomas. It is also present in abnormal lymphocytes associated with some cases of Hodgkins disease. Because even on B cell precursors, it can be used to stain a wider range of cells compared to the alternative B cell marker CD20 and is often used together in immunohistochemistry panels. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CD79a. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD79a is a disulphide-linked heterodimer together with CD79b. CD79a plays multiple and diverse roles in B cell development and function. The CD79a/b heterodimer associates non-covalently with the immunoglobulin heavy chain through its transmembrane region, thus forming the BCR along with the immunoglobulin light chain and the pre-BCR when associated with the surrogate light chain in developing B cells. Association of the CD79a/b heterodimer with the immunoglobulin heavy chain is required for surface expression of the BCR and BCR induced calcium flux and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. The CD79a protein is present on the surface of B-cells throughout their life cycle, and is absent on all other healthy cells, making it a highly reliable marker for B-cells in immunohistochemistry. The protein remains present when B cells transform into active plasma cells, and is also present in virtually all B-cell neoplasms, including B-cell lymphomas, plasmacytomas and myelomas. It is also present in abnormal lymphocytes associated with some cases of Hodgkins disease. Because even on B cell precursors, it can be used to stain a wider range of cells compared to the alternative B cell marker CD20 and is often used together in immunohistochemistry panels.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161