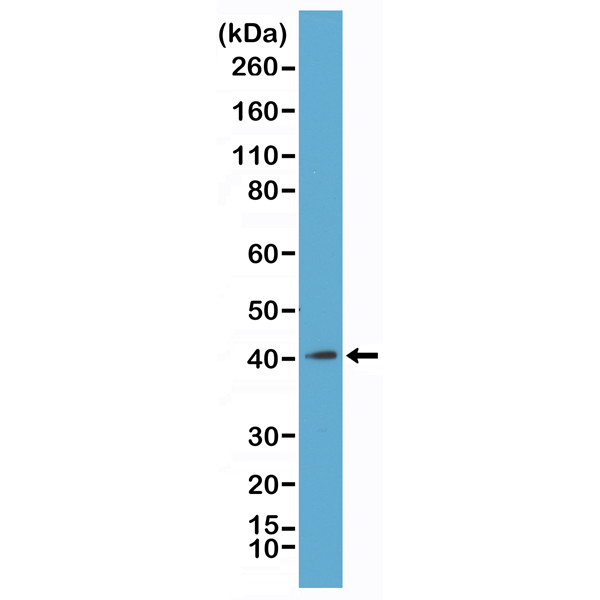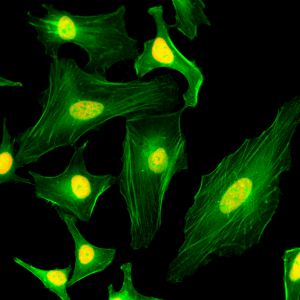
Immunocytochemistry of HeLa cells, using anti-Histone macroH2A1/macroH2A2 Rabbit mAb RM248 (red). Actin filaments have been labeled with fluorescein phalloidin (green).
anti-Core Histone Macro-H2A.1 (H2AFY), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM248)
REV-31-1118-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityVertebrate
TargetMacroh2a1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Core Histone Macro-H2A.1 (H2AFY), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM248)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM248
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Gene ID26914
- Target nameMacroh2a1
- Target descriptionmacroH2A.1 histone
- Target synonymsH2AF12M, H2afy, mH2a1, core histone macro-H2A.1, H2A histone family, member Y, H2A.y, H2A/y, MACROH2A1.2, histone macroH2A1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9QZQ8
- Protein NameCore histone macro-H2A.1
- Scientific DescriptionHistones are proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes. Histones are responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of a nucleosome. One chromatin molecule is composed of at least one of each core histones per 100 base pairs of DNA. There are five families of histones known to date; these histones are termed H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H2A is considered a core histone, along with H2B, H3 and H4. Core formation first occurs through the interaction of two H2A molecules. Then, H2A forms a dimer with H2B; the core molecule is complete when H3-H4 also attaches to form a tetramer. Histone H2A is composed of non-allelic variants, including H2A.1, H2A.2, H2A.X, and H2A.Z. H2A packages DNA molecules into chromatin and has been correlated with DNA modification and epigenetics. H2A plays a major role in determining the overall structure of chromatin and regulates gene expression. Protein modification on histone H2A exist and can sometimes result in a change in function. Different H2A variants were exploited to have different functions, genetic sequences and modifications. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the Core histone macro-H2A.1 (Histone macroH2A1) protein, independent of post-translational modifications. No cross reactivity with other histone proteins. Applications: WB, ELISA, Multiplex, ICC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Histones are proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes. Histones are responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of a nucleosome. One chromatin molecule is composed of at least one of each core histones per 100 base pairs of DNA. There are five families of histones known to date; these histones are termed H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H2A is considered a core histone, along with H2B, H3 and H4. Core formation first occurs through the interaction of two H2A molecules. Then, H2A forms a dimer with H2B; the core molecule is complete when H3-H4 also attaches to form a tetramer. Histone H2A is composed of non-allelic variants, including H2A.1, H2A.2, H2A.X, and H2A.Z. H2A packages DNA molecules into chromatin and has been correlated with DNA modification and epigenetics. H2A plays a major role in determining the overall structure of chromatin and regulates gene expression. Protein modification on histone H2A exist and can sometimes result in a change in function. Different H2A variants were exploited to have different functions, genetic sequences and modifications.
- ReactivityVertebrate
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161