Anti-Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers (CPDs) mAb (Clone TDM-2)
CAC-NM-DND-001
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
Overview
- SupplierCosmo Bio USA
- Product NameAnti-Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers (CPDs) mAb (Clone TDM-2)
- Delivery Days Customer16
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDClone tdm-2
- HostMouse
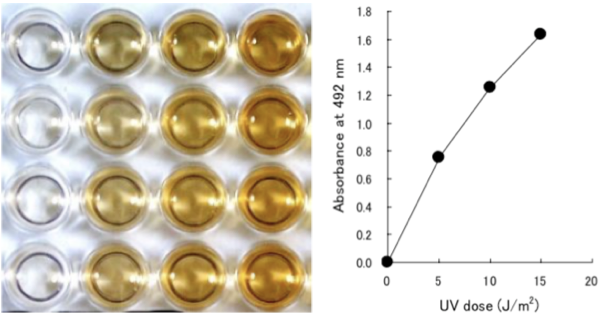
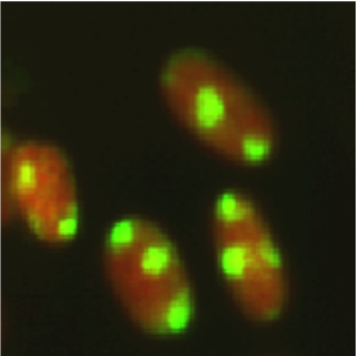
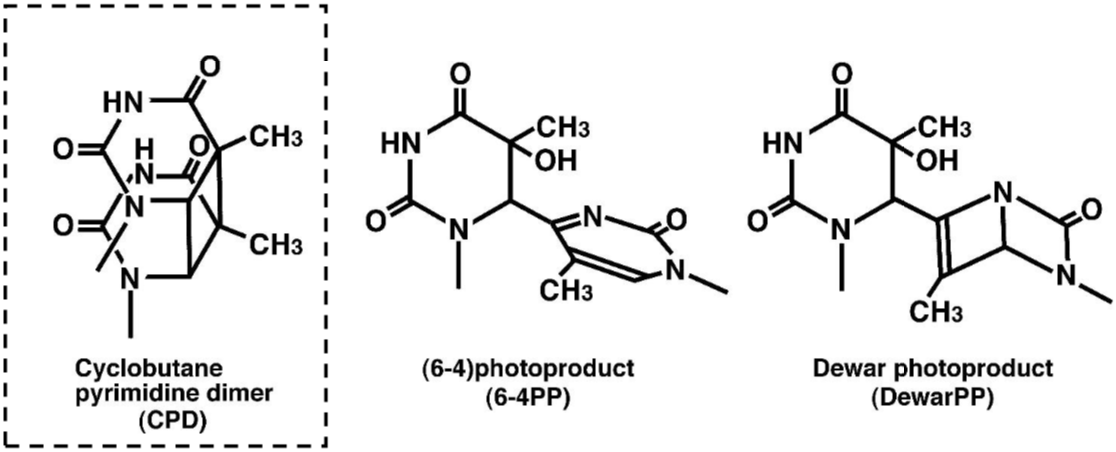
- Scientific DescriptionCyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD)-specific mAb TDM-2 was cloned by fusing mouse myeloma cells with splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with methylated BSA conjugated with UVC-irradiated calf thymus DNA. TDM-2 binds CPDs in denatured DNA from all organisms from bacteria to human and is validated for ELISA and indirect immunofluorescence. Background DNA damage in cells exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation plays significant roles in cell-cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair, cell killing, mutation, and neoplastic transformation. The major types of DNA damage induced by UVB (280-315 nm, component of sunlight) and by UVC (200-280 nm) are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and (6-4) photoproducts (6-4PPs), which are formed between adjacent pyrimidine nucleotides on the same strand of DNA. Approximately 70-80% of UV-induced DNA damage is CPDs and the remainder is 6-4PPs and Dewar isomers of 6-4PPs. In normal human cells, these types of DNA lesions are repaired by the nucleotide excision repair system. (19) have established monoclonal antibodies specific for CPDs and 6-4PPs. These antibodies enable quantitation of photoproducts in DNA purified from cultured cells or from the skin epidermis by ELISA and to visualize and measure photoproducts in DNA in cultured cells or the skin by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF). This technology will contribute to studies of molecular mechanisms of cellular responses to UV and DNA damage in many research fields including cancer research, photobiology, dermatology, ophthalmology, immunology, and cosmetology. Reactivity CPDs in single-stranded DNA CPDs formed in every dipyrimidine sequence (TT, TC, CT and CC) CPDs formed in oligonucleotides consisting of more than eight bases Applications Immunocytochemistry 1:1500 ELISA 1:1000 Source The CPD-specific hybridoma (clone TDM-2) was established by fusion of mouse myeloma cells with splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with methylated BSA conjugated with UVC-irradiated calf thymus DNA. Hybridoma culture supernatant was collected and precipitated with ice-cold ammonium sulfate. After centrifugation, the pellet, dissolved in small volume of double-distilled water, was dialyzed against PBS and lyophilized. Formulation Lyophilate to be reconstituted in 100 ml of distilled water Contains no preservative Storage Lyophilized form -20°C Reconstituted form -20°C Stable for at least 1 year; aliquot to avoid freezing and thawing
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC41116161