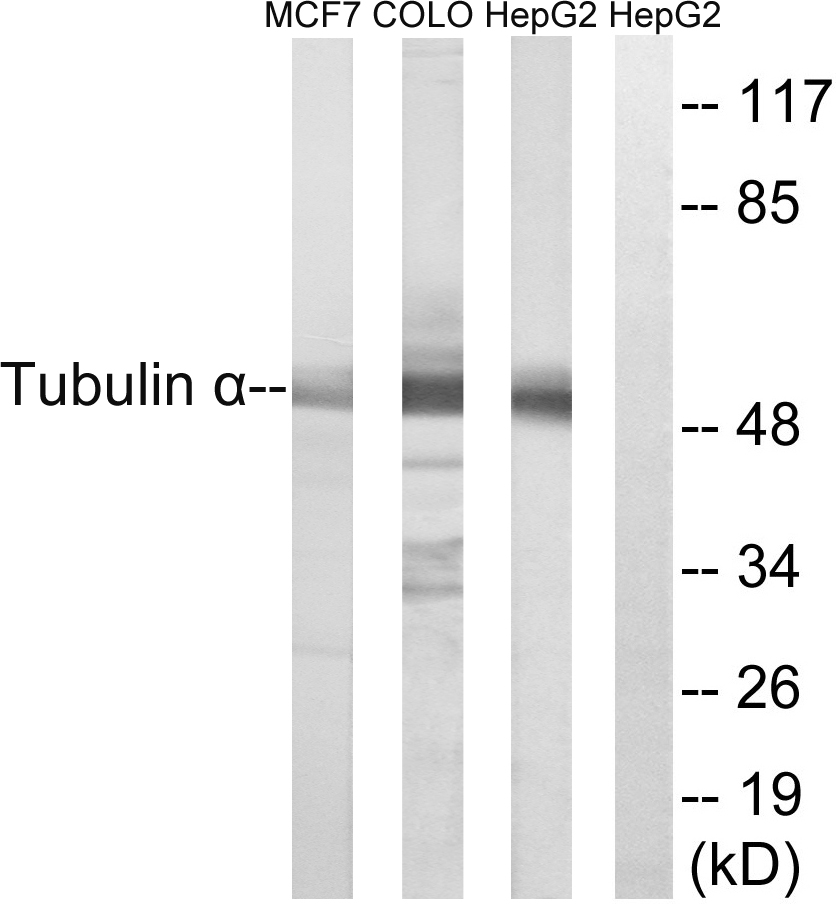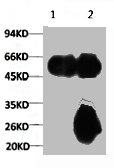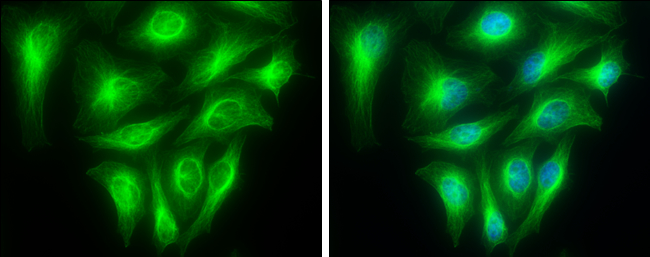
anti-Detyrosinated alpha-Tubulin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM444)
REV-31-1335-00
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTUBA1A
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Detyrosinated alpha-Tubulin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM444)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM444
- Gene ID7846
- Target nameTUBA1A
- Target descriptiontubulin alpha 1a
- Target synonymsB-ALPHA-1, LIS3, TUBA3, tubulin alpha-1A chain, hum-a-tub1, hum-a-tub2, tubulin B-alpha-1, tubulin alpha-3 chain, tubulin, alpha, brain-specific
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ71U36
- Protein NameTubulin alpha-1A chain
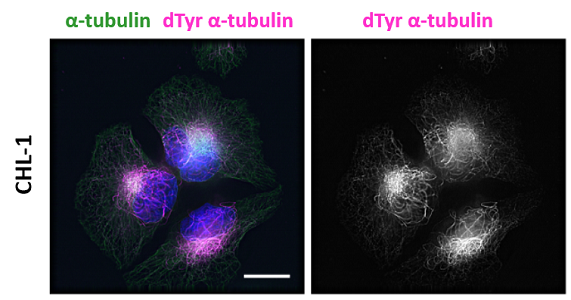
- Scientific DescriptionMicrotubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different alpha- and beta-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on alpha- and beta-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Detyrosination is a form of posttranslational modification that occurs on alpha-tubulin. It consists of the removal of the C-terminal tyrosine to expose a glutamate at the newly formed C-terminus. Tubulin polymers, called microtubules, that contain detyrosinated alpha-tubulin are usually referred to as Glu-microtubules while unmodified polymers are called Tyr-microtubules. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to detyrosinated human alpha-Tubulin. It has no cross reactivity to non-detyrosinated alpha-Tubulin. Apllication: WB, ICC, IF. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Microtubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different alpha- and beta-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on alpha- and beta-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Detyrosination is a form of posttranslational modification that occurs on alpha-tubulin. It consists of the removal of the C-terminal tyrosine to expose a glutamate at the newly formed C-terminus. Tubulin polymers, called microtubules, that contain detyrosinated alpha-tubulin are usually referred to as Glu-microtubules while unmodified polymers are called Tyr-microtubules.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161