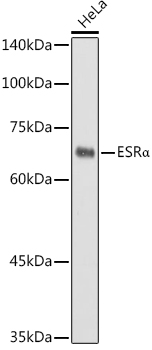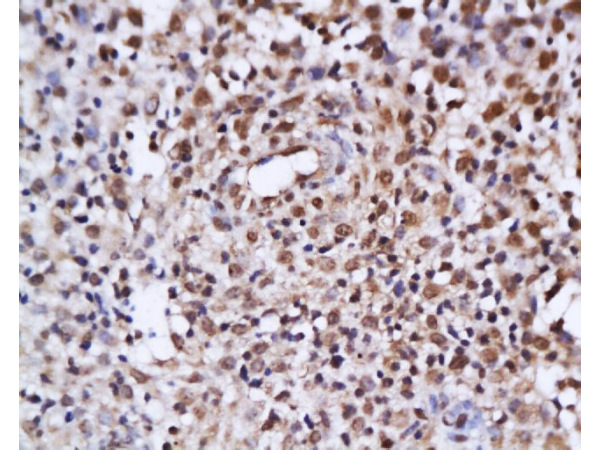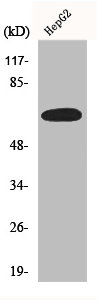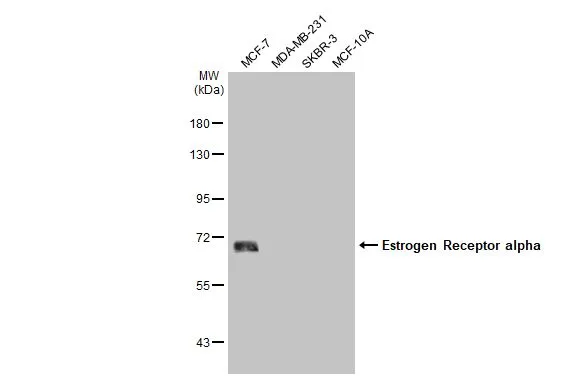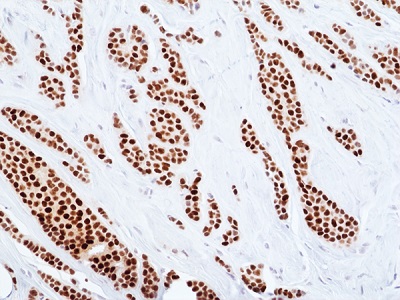
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using anti-ER-alpha rabbit monoclonal antibody clone RM494 at a 1:100 dilution.
anti-ER-alpha (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM494)
REV-31-1386-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetESR1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-ER-alpha (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM494)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM494
- Gene ID2099
- Target nameESR1
- Target descriptionestrogen receptor 1
- Target synonymsER, ESR, ESRA, ESTRR, Era, NR3A1, estrogen receptor, E2 receptor alpha, ER-alpha, estradiol receptor, estrogen nuclear receptor alpha, estrogen receptor alpha E1-E2-1-2, estrogen receptor alpha E1-N2-E2-1-2, nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1, oestrogen receptor alpha
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP03372
- Protein NameEstrogen receptor
- Scientific DescriptionEstrogen Receptors (ER) are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear receptors. The estrogen receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor, that when bound to estrogen hormone, induces a conformational change that allows dimerization and binding to estrogen response elements (ERE) in DNA. When bound to EREs, ER can positively or negatively regulate gene transcription through the recruitment of coactivator or corepressor proteins. There are two different forms of the estrogen receptor, alpha and beta, encoded by separate genes (ESR1 and ESR2, respectively). Estrogen receptors are involved in pathological processes including breast cancer, endometrial cancer and osteoporosis. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human ER-alpha (Estrogen receptor). Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: Recombinant human ER-alpha. Application: IHC, WB. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Estrogen Receptors (ER) are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear receptors. The estrogen receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor, that when bound to estrogen hormone, induces a conformational change that allows dimerization and binding to estrogen response elements (ERE) in DNA. When bound to EREs, ER can positively or negatively regulate gene transcription through the recruitment of coactivator or corepressor proteins. There are two different forms of the estrogen receptor, alpha and beta, encoded by separate genes (ESR1 and ESR2, respectively). Estrogen receptors are involved in pathological processes including breast cancer, endometrial cancer and osteoporosis.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161