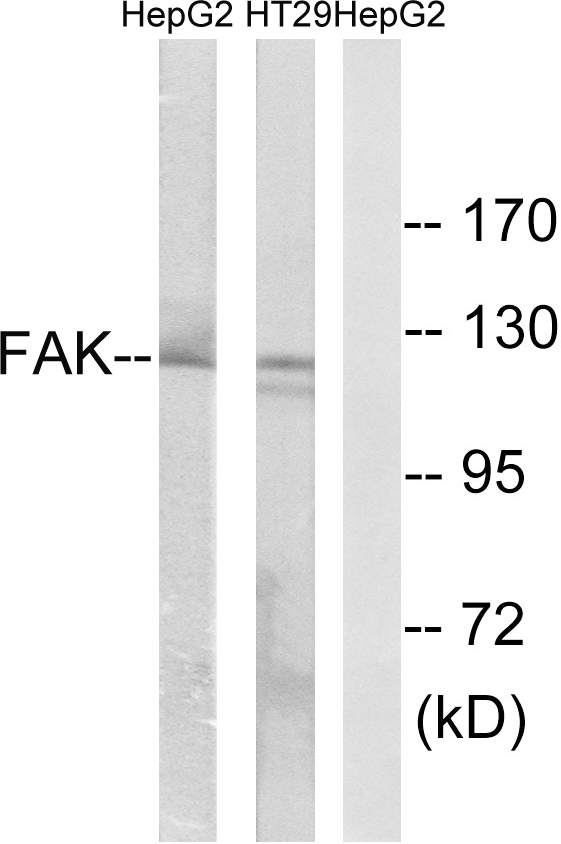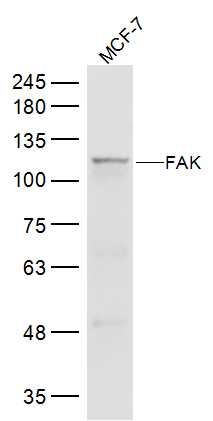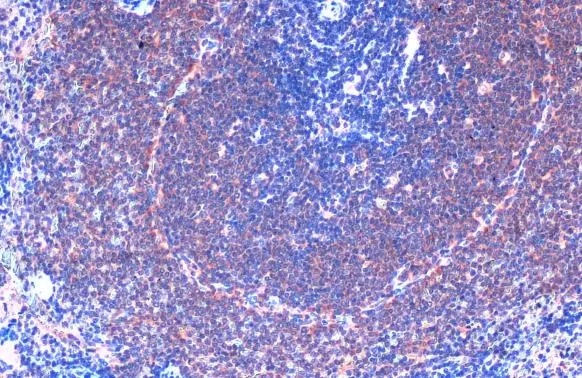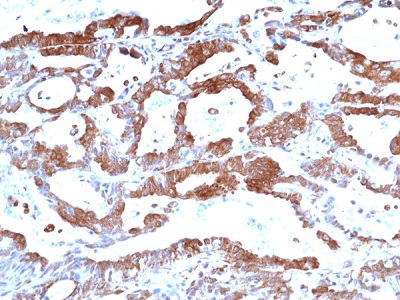
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human lung cancer tissue sections using Anti-FAK antibody (RM472) at 1:100 dilution.
anti-FAK (Focal adhesion kinase 1), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM472)
REV-31-1364-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPTK2
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-FAK (Focal adhesion kinase 1), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM472)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM472
- Gene ID5747
- Target namePTK2
- Target descriptionprotein tyrosine kinase 2
- Target synonymsFADK, FADK 1, FAK, FAK1, FRNK, PPP1R71, p125FAK, pp125FAK, focal adhesion kinase 1, FAK-related non-kinase polypeptide, PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2, focal adhesion kinase-related nonkinase, protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 71
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ05397
- Protein NameFocal adhesion kinase 1
- Scientific DescriptionFAK1 (Focal Adhesion Kinase 1) is a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase that is involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, migration, and survival. It is a member of the Src family of kinases. FAK1 is activated by binding to integrins, which are transmembrane proteins that mediate the attachment of cells to the extracellular matrix. When FAK1 is activated, it phosphorylates a number of downstream targets, including paxillin, tensin, and the small GTPase Ras. These phosphorylation events lead to the activation of a number of signaling pathways, including the MAPK pathway, the PI3K-AKT pathway, and the NF-kappaB pathway. The MAPK pathway is involved in the regulation of cell migration, survival, and proliferation. The PI3K-AKT pathway is involved in the regulation of cell survival and metabolism. The NF-kappaB pathway is involved in the regulation of inflammation and immunity. - Recombinant Antibody. RM472 reacts to human FAK (Focal adhesion kinase 1). This antibody may also react to mouse or rat FAK, as predicted by immunogen homology. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Tyr397 of human FAK1 (Focal adhesion kinase 1). Applications: IHC, WB. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. FAK1 (Focal Adhesion Kinase 1) is a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase that is involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, migration, and survival. It is a member of the Src family of kinases. FAK1 is activated by binding to integrins, which are transmembrane proteins that mediate the attachment of cells to the extracellular matrix. When FAK1 is activated, it phosphorylates a number of downstream targets, including paxillin, tensin, and the small GTPase Ras. These phosphorylation events lead to the activation of a number of signaling pathways, including the MAPK pathway, the PI3K-AKT pathway, and the NF-kappaB pathway. The MAPK pathway is involved in the regulation of cell migration, survival, and proliferation. The PI3K-AKT pathway is involved in the regulation of cell survival and metabolism. The NF-kappaB pathway is involved in the regulation of inflammation and immunity.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161