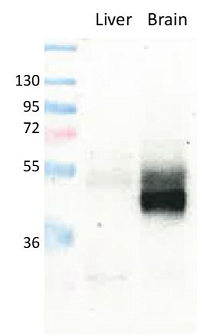
Figure 1: Detection of endogenous mouse GLUT1 in brain and liver (negative/low expression) membranes by immunoblotting using anti-GLUT1, pAb (IN116) (Prod. No. AG-25B-0040).
anti-GLUT1, pAb (IN116)
AG-25B-0040
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetSLC2A1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-GLUT1, pAb (IN116)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID6513
- Target nameSLC2A1
- Target descriptionsolute carrier family 2 member 1
- Target synonymsCSE, DYT17, DYT18, DYT9, EIG12, GLUT, GLUT-1, GLUT1, GLUT1DS, HTLVR, PED, SDCHCN, solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1, choreoathetosis/spasticity, episodic (paroxysmal choreoathetosis/spasticity), dystonia gene 18, dystonia gene 9, glucose transporter type 1, erythrocyte/brain, hepG2 glucose transporter, human T-cell leukemia virus (I and II) receptor, receptor for HTLV-1 and HTLV-2, solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 1
- HostRabbit
- Protein IDP11166
- Protein NameSolute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1
- Scientific DescriptionGLUT1 belongs to the family of glucose transporters (GLUTs, encoded by the SLC2A genes), which comprises 14 isoforms. GLUT1, the uniporter protein encoded by the SLC2A1 gene, is a key rate-limiting factor in the transport of glucose. It is composed of twelve transmembrane segments of the protein and an intracellular N- and C-terminus are forming the protein pore. In normal tissues, GLUT1 is limited to being expressed on erythrocytes and endothelial cells in the blood-brain barriers. GLUT1 is located at the blood-brain barrier and assures the transport of glucose (the most important energy carrier of the brain) into the brain. The genetic defect of Glut1 is known as the Glut1 deficiency syndrome (Glut1-DS) and is characterized by early infantile seizures, developmental delay, microcephaly and ataxia. GLUT1 is a pivotal rate-limiting element in the transport of glucose in malignancy cells and is overexpressed in different types of human cancers. GLUT1 is involved in the progression and metastasis of cancer cells. - Polyclonal Antibody. Recognizes human, mouse and rat GLUT1. Does not detect GLUT2. Applications: IHC, IP, WB. Source: Rabbit. GLUT1 belongs to the family of glucose transporters (GLUTs, encoded by the SLC2A genes), which comprises 14 isoforms. GLUT1, the uniporter protein encoded by the SLC2A1 gene, is a key rate-limiting factor in the transport of glucose. It is composed of twelve transmembrane segments of the protein and an intracellular N- and C-terminus are forming the protein pore. In normal tissues, GLUT1 is limited to being expressed on erythrocytes and endothelial cells in the blood-brain barriers. GLUT1 is located at the blood-brain barrier and assures the transport of glucose (the most important energy carrier of the brain) into the brain. The genetic defect of Glut1 is known as the Glut1 deficiency syndrome (Glut1-DS) and is characterized by early infantile seizures, developmental delay, microcephaly and ataxia. GLUT1 is a pivotal rate-limiting element in the transport of glucose in malignancy cells and is overexpressed in different types of human cancers. GLUT1 is involved in the progression and metastasis of cancer cells.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161






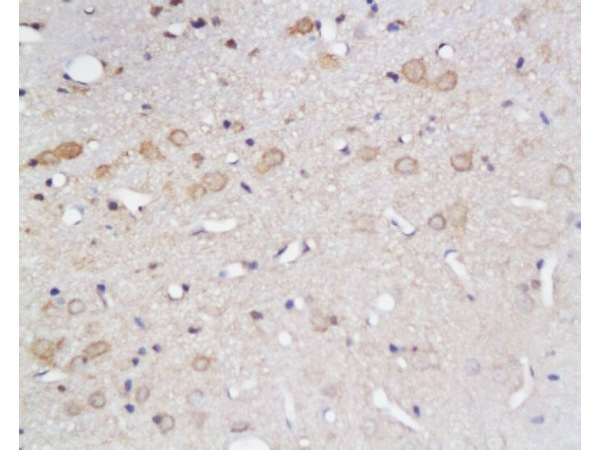
![IHC-P analysis of human cerebrum (grey matter) tissue using GTX04469 GluT1 antibody [MSVA-401R] HistoMAX?. A particularly strong GluT1 staining of endothelial cells is seen in the brain.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04469/GTX04469_20230728_IHC-P_56_23072722_577.webp)