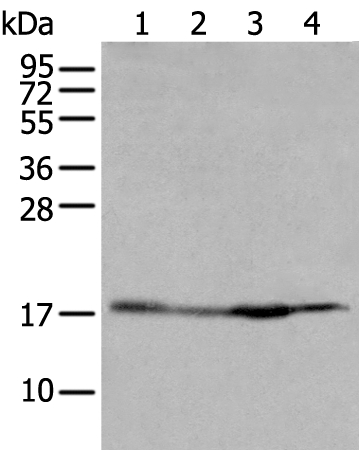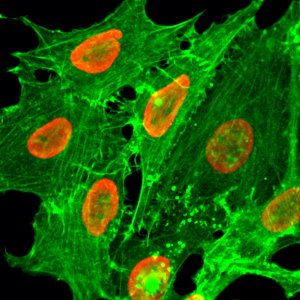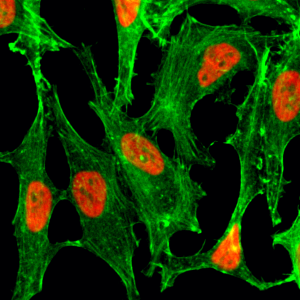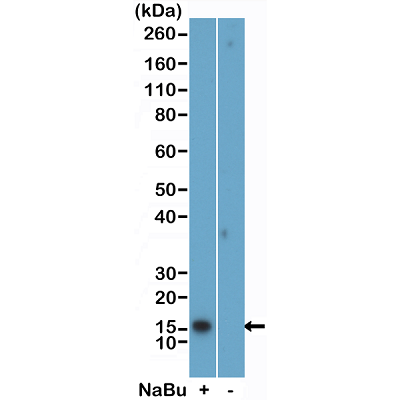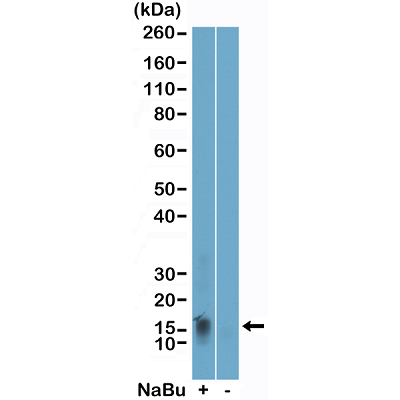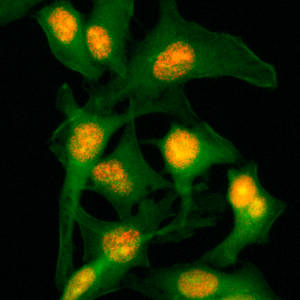
Immunocytochemical staining of HeLa cells, using Anti-Histone H2B Rabbit mAb RM230 (red). Actin filaments have been labeled with fluorescein phalloidin (green).
anti-Histone H2B, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM230)
REV-31-1112-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityVertebrate
TargetH2BC11
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Histone H2B, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM230)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM230
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Gene ID8970
- Target nameH2BC11
- Target descriptionH2B clustered histone 11
- Target synonymsH2B/r, H2BFR, H2BJ, HIST1H2BJ, histone H2B type 1-J, H2B histone family, member R, histone 1, H2bj, histone H2B.1, histone H2B.r, histone cluster 1 H2B family member j, histone cluster 1, H2bj
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP06899
- Protein NameHistone H2B type 1-J
- Scientific DescriptionHistones are proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes. Histones are responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of a nucleosome. One chromatin molecule is composed of at least one of each core histones per 100 base pairs of DNA. There are five families of histones known to date; these histones are termed H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H2B is considered a core histone, along with H2A, H3 and H4. H2A packages DNA molecules into chromatin and has been correlated with DNA modification and epigenetics. H2A plays a major role in determining the overall structure of chromatin and regulates gene expression. Protein modification on histone H2A exist and can sometimes result in a change in function. Different H2A variants were exploited to have different functions, genetic sequences and modifications. Histone H2B is a structural protein that helps organize eukaryotic DNA. It plays an important role in the biology of the nucleus where it is involved in the packaging and maintaining of chromosomes, regulation of transcription and replication and repair of DNA. Histone H2B helps regulate chromatin structure and function through post-translational modifications and specialized histone variants. Hyperacetylation of histone tails helps DNA-binding proteins access chromatin by weakening histone-DNA and nucleosome-nucleosome interactions. Acetylation of a specific lysine residue binds to bromine-containing domains of certain transcription and chromatin regulatory proteins. This docking facilitates the recruitment of these proteins to the correct region of the chromosome. Ubiquitinated histone H2B is often found in regions of active transcription and stimulates transcriptional elongation and sets the stage for further modifications that regulate multiple elements of transcription. In histone H2B, a phosphorylated serine or threonine residue activates transcription. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the Histone H2B protein, independent of post-translational modifications. No cross reactivity with other histone proteins. Applications: WB, ELISA, Multiplex, ICC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Histones are proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes. Histones are responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of a nucleosome. One chromatin molecule is composed of at least one of each core histones per 100 base pairs of DNA. There are five families of histones known to date; these histones are termed H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H2B is considered a core histone, along with H2A, H3 and H4. H2A packages DNA molecules into chromatin and has been correlated with DNA modification and epigenetics. H2A plays a major role in determining the overall structure of chromatin and regulates gene expression. Protein modification on histone H2A exist and can sometimes result in a change in function. Different H2A variants were exploited to have different functions, genetic sequences and modifications. Histone H2B is a structural protein that helps organize eukaryotic DNA. It plays an important role in the biology of the nucleus where it is involved in the packaging and maintaining of chromosomes, regulation of transcription and replication and repair of DNA. Histone H2B helps regulate chromatin structure and function through post-translational modifications and specialized histone variants. Hyperacetylation of histone tails helps DNA-binding proteins access chromatin by weakening histone-DNA and nucleosome-nucleosome interactions. Acetylation of a specific lysine residue binds to bromine-containing domains of certain transcription and chromatin regulatory proteins. This docking facilitates the recruitment of these proteins to the correct region of the chromosome. Ubiquitinated histone H2B is often found in regions of active transcription and stimulates transcriptional elongation and sets the stage for further modifications that regulate multiple elements of transcription. In histone H2B, a phosphorylated serine or threonine residue activates transcription.
- ReactivityVertebrate
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161