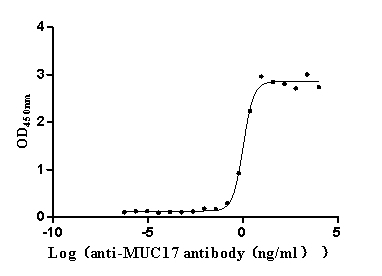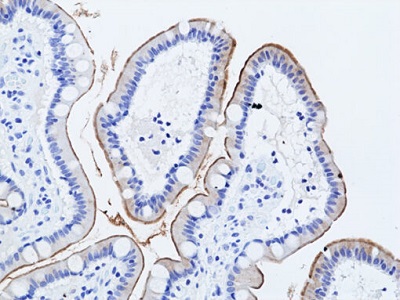
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human small intestine tissue sections using anti-Muc17 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM517) at 1:100 dilution for 1 hr at room temperature.
anti-MUC-17 (Mucin-17) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM517)
REV-31-1409-00
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetMUC17
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-MUC-17 (Mucin-17) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM517)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM517
- Gene ID140453
- Target nameMUC17
- Target descriptionmucin 17, cell surface associated
- Target synonymsMUC-17, MUC-3, MUC3, mucin-17, membrane mucin MUC17, secreted mucin MUC17, small intestinal mucin MUC3, small intestinal mucin-3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ685J3
- Protein NameMucin-17
- Scientific DescriptionMembrane mucins have several functions in epithelial cells including cytoprotection, extravasation during metastases, maintenance of luminal structure, and signal transduction. MUC-17, contains an extended, repetitive extracellular glycosylation domain and a carboxyl terminus with two EGF-like domains, a SEA module domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain with potential serine and tyrosine phosphorylation sites. MUC-17 interacts via its C-terminus with PDZK1 and this interaction appears important for proper localization. MUC-17 probably plays a role in maintaining homeostasis on mucosal surfaces. Increased expression of this molecule has been reported in colon cancer. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Muc-17 (Mucin-17). Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A peptide corresponding to residues near the C-terminus of human Muc17. Applications: IHC. Membrane mucins have several functions in epithelial cells including cytoprotection, extravasation during metastases, maintenance of luminal structure, and signal transduction. MUC-17, contains an extended, repetitive extracellular glycosylation domain and a carboxyl terminus with two EGF-like domains, a SEA module domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain with potential serine and tyrosine phosphorylation sites. MUC-17 interacts via its C-terminus with PDZK1 and this interaction appears important for proper localization. MUC-17 probably plays a role in maintaining homeostasis on mucosal surfaces. Increased expression of this molecule has been reported in colon cancer.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161