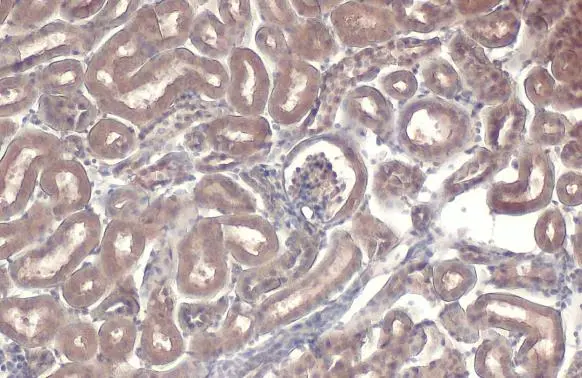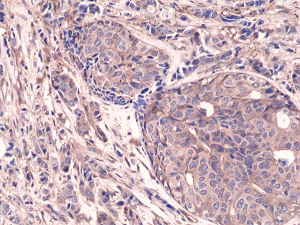
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using Anti-NFkB p65 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM273) at a 1:1250 dilution.
anti-NF-kappa-B p65 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM273)
REV-31-1154-00
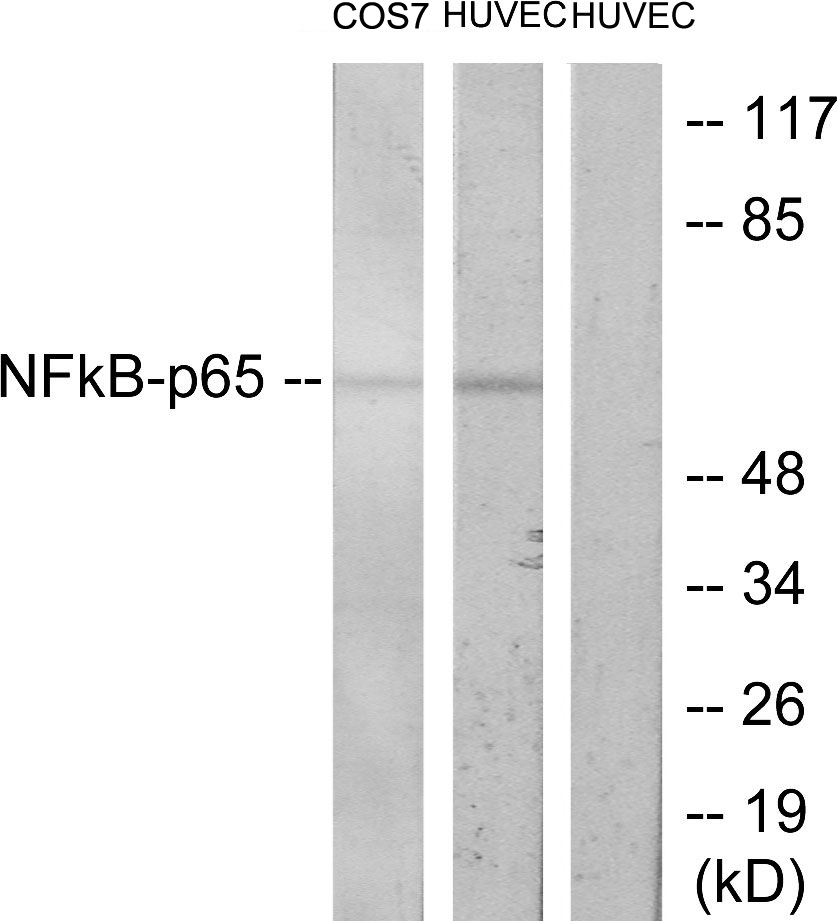
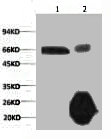
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetRELA
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-NF-kappa-B p65 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM273)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM273
- Gene ID5970
- Target nameRELA
- Target descriptionRELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit
- Target synonymsAIF3BL3, CMCU, NFKB3, p65, transcription factor p65, NF-kappa-B p65delta3, NF-kappa-B transcription factor p65, nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3, v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ04206
- Protein NameTranscription factor p65
- Scientific DescriptionNF-kappaB is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappaB is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The heterodimeric p65-p50 complex is the most abundant complex. The dimers bind at kappaB sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappaB sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappaB complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappaB inhibitor (I-kappaB) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappaB is phosphorylated by I-kappaB kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappaB complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappaB heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappaB p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappaB complex. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human transcription factor p65 (NF-kB p65 subunit). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. NF-kappaB is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappaB is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The heterodimeric p65-p50 complex is the most abundant complex. The dimers bind at kappaB sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappaB sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappaB complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappaB inhibitor (I-kappaB) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappaB is phosphorylated by I-kappaB kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappaB complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappaB heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappaB p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappaB complex.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161