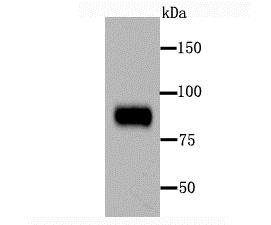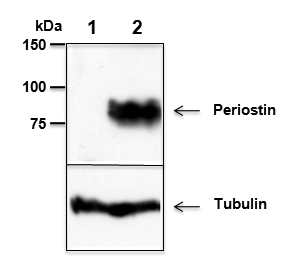
Mouse Periostin is detected by immunoblotting using anti-Periostin, mAb (Stiny-1) (Prod. No AG-20B-0033). Whole tissue extracts from mouse liver (lane 1) or mammary tumor (lane 2) were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, transferred to
anti-Periostin [OSF-2], mAb (Stiny-1)
AG-20B-0033
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetPOSTN
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-Periostin [OSF-2], mAb (Stiny-1)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDStiny-1
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID10631
- Target namePOSTN
- Target descriptionperiostin
- Target synonymsOSF-2, OSF2, PDLPOSTN, PN, periostin, osteoblast specific factor 2 (fasciclin I-like), periodontal ligament-specific periostin, periostin, osteoblast specific factor
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ15063
- Protein NamePeriostin
- Scientific DescriptionMonoclonal Antibody. Recognizes human and mouse periostin. Isotype: Mouse IgG1kappa. Clone: Stiny-1. Applications: ELISA, IHC, WB. Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. Periostin is a 90-kDa matricellular protein that consists of a typical signal sequence, followed by a cysteine-rich region, an EMI domain (protein-protein interactions), four tandem fasciclin-like domains that are responsible for integrin binding, and a C-terminal region. Periostin was originally isolated as an osteoblast-specific factor that functions as a cell adhesion molecule for pre-osteoblasts and in osteoblast recruitment, attachment and spreading. Periostin is also involved in many fundamental biological processes such as cell proliferation, cell invasion and angiogenesis. Periostin expression is increased by both transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). Changes in periostin expression are commonly detected in various cancers and pre-cancerous conditions, and periostin may be involved in regulating cancer cell activities that contribute to tumorigenesis, cancer progression and metastasis. Periostin has shown to be involved in many aspects of allergic inflammation, such as eosinophil recruitment, airway remodeling, development of a Th2 phenotype and increased expression of inflammatory mediators. It is evaluated as a biomarker for bronchial asthma and airway inflammation. - Periostin is a 90-kDa matricellular protein that consists of a typical signal sequence, followed by a cysteine-rich region, an EMI domain (protein-protein interactions), four tandem fasciclin-like domains that are responsible for integrin binding, and a C-terminal region. Periostin was originally isolated as an osteoblast-specific factor that functions as a cell adhesion molecule for pre-osteoblasts and in osteoblast recruitment, attachment and spreading. Periostin is also involved in many fundamental biological processes such as cell proliferation, cell invasion and angiogenesis. Periostin expression is increased by both transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). Changes in periostin expression are commonly detected in various cancers and pre-cancerous conditions, and periostin may be involved in regulating cancer cell activities that contribute to tumorigenesis, cancer progression and metastasis. Periostin has shown to be involved in many aspects of allergic inflammation, such as eosinophil recruitment, airway remodeling, development of a Th2 phenotype and increased expression of inflammatory mediators. It is evaluated as a biomarker for bronchial asthma and airway inflammation.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203