![Binding of Progranulin (human) (rec.) (untagged) (Prod. No. AG-40A-0188Y) to Sortilin (human) (rec.) (His) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0229) is inhibited by the antibody Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Bioimilar] (Prod. No. AG-27B-7000PF). Methods: Progranulin (human) (rec.) (untagged) is coated on an ELISA plate at 1 microg/ml. Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Biosimilar] or an unrelated mAb (Control) is added (starting at 20 microg/ml with a twofold serial dilution) together with 250 ng/ml of Sortilin (rec.) (His) for 1 hour. The binding is detected using an anti-His (HRP) incubated for 30 minutes followed by addition of the substrate TMB. The decreasing ODs observed in the Y axis represent the binding between Progranulin and Sortilin that is inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Biosimilar]. This inhibition is not observed with the control antibody. Binding of Progranulin (human) (rec.) (untagged) (Prod. No. AG-40A-0188Y) to Sortilin (human) (rec.) (His) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0229) is inhibited by the antibody Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Bioimilar] (Prod. No. AG-27B-7000PF). Methods: Progranulin (human) (rec.) (untagged) is coated on an ELISA plate at 1 microg/ml. Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Biosimilar] or an unrelated mAb (Control) is added (starting at 20 microg/ml with a twofold serial dilution) together with 250 ng/ml of Sortilin (rec.) (His) for 1 hour. The binding is detected using an anti-His (HRP) incubated for 30 minutes followed by addition of the substrate TMB. The decreasing ODs observed in the Y axis represent the binding between Progranulin and Sortilin that is inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Biosimilar]. This inhibition is not observed with the control antibody.](https://adipogen.com/pub/media/catalog/product/a/g/ag-27b-7000pf-binding_blocking_assay-500px.jpg)
Binding of Progranulin (human) (rec.) (untagged) (Prod. No. AG-40A-0188Y) to Sortilin (human) (rec.) (His) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0229) is inhibited by the antibody Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Bioimilar] (Prod. No. AG-27B-7000PF). Methods: Progranulin (human) (rec.) (untagged) is coated on an ELISA plate at 1 microg/ml. Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Biosimilar] or an unrelated mAb (Control) is added (starting at 20 microg/ml with a twofold serial dilution) together with 250 ng/ml of Sortilin (rec.) (His) for 1 hour. The binding is detected using an anti-His (HRP) incubated for 30 minutes followed by addition of the substrate TMB. The decreasing ODs observed in the Y axis represent the binding between Progranulin and Sortilin that is inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) [Latozinemab Biosimilar]. This inhibition is not observed with the control antibody.
anti-Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (preservative free) [Latozinemab]
AG-27B-7000PF
ApplicationsNeutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSORT1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-Sortilin (human), mAb (rec.) (blocking) (preservative free) [Latozinemab]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsNeutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDLatozinemab
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID6272
- Target nameSORT1
- Target descriptionsortilin 1
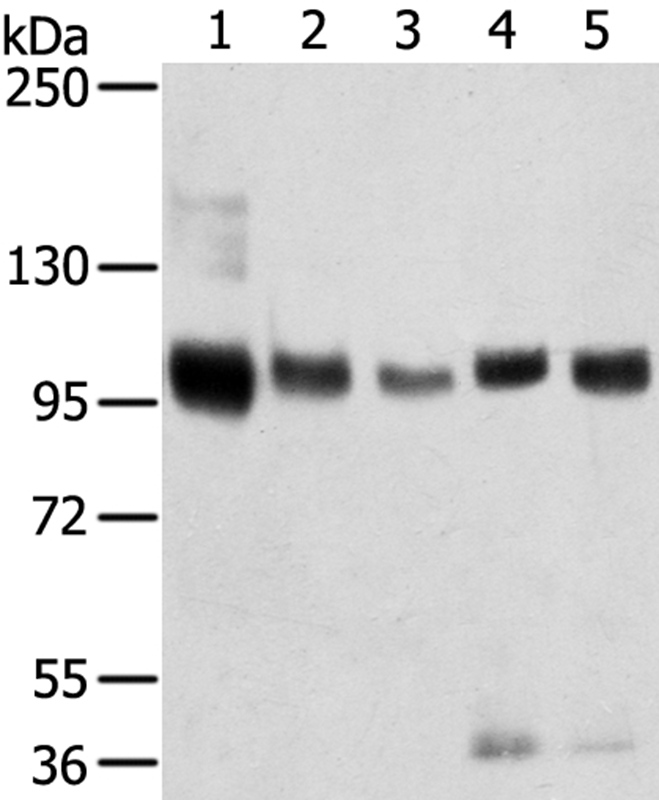
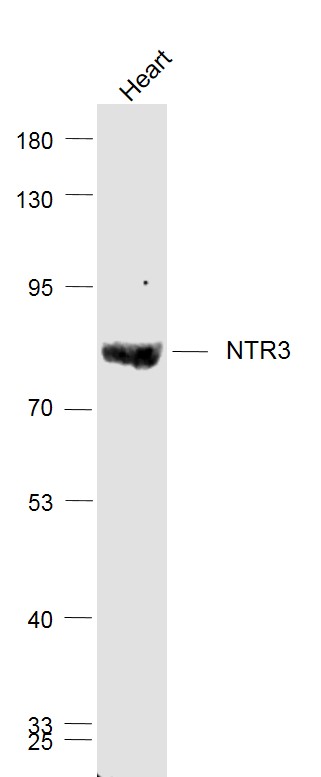
- Target synonymsGp95, LDLCQ6, NT3, NTR3, sortilin, 100 kDa NT receptor, glycoprotein 95, neurotensin receptor 3
- HostHuman
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ99523
- Protein NameSortilin
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. Recognizes and binds to human sortilin. Source: CHO cells. Isotype: Human IgG1kappa. Immunogen: Recombinant human Sortilin. Applications: FUNC (Blocking). Sortilin is a type I transmembrane multiligand receptor that is a member of the Vacuolar protein sorting 10 protein (Vps10p) domain receptor family. It is a 95 kDa protein, ubiquitously expressed, although most abundantly expressed in neurons, hepatocytes, adipocytes and white blood cells including macrophages. Sortilin is synthesized as a propeptide in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and processed to its mature form by furin-mediated cleavage in the trans-Golgi network. The SORL1 gene is one of the strongest genetic risk factors for Alzheimers disease and is associated with frontotemporal dementia. The primary function of sortilin is trafficking proteins from the Golgi to secretory vesicles and endolysosomal compartments. The majority of trafficking is from the Golgi to the endosomal compartment where sortilin deposits cargo targeted for catabolism in the lysosome and then is trafficked back to the Golgi via a retromer complex. At the cell surface, sortilin can remain intact and act as a receptor for extracellular ligands that can initiate signaling cascades or be internalized as a method of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Additionally, cell surface sortilin protein can undergo an additional cleavage that results in the release of the soluble form of the protein into the extracellular space. The sortilin receptor binds the nerve growth factor precursor (proNGF), neurotensin and Progranulin (PGRN), a secreted growth factor implicated in a multitude of processes ranging from regulation of inflammation to wound healing, tumorigenesis and neurological diseases. Sortilin controls PGRN trafficking and lysosomal degradation, but PGRN exerts its multiple functions independent of sortilin. Sortilin down-regulation via blocking antibodies, such as Latozinemab Biosimilar, is a key mechanism in increasing PGRN levels suggesting that sortilin is a potential target to correct PGRN reduction, such as that in patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) caused by GRN mutations. - Sortilin is a type I transmembrane multiligand receptor that is a member of the Vacuolar protein sorting 10 protein (Vps10p) domain receptor family. It is a 95 kDa protein, ubiquitously expressed, although most abundantly expressed in neurons, hepatocytes, adipocytes and white blood cells including macrophages. Sortilin is synthesized as a propeptide in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and processed to its mature form by furin-mediated cleavage in the trans-Golgi network. The SORL1 gene is one of the strongest genetic risk factors for Alzheimers disease and is associated with frontotemporal dementia. The primary function of sortilin is trafficking proteins from the Golgi to secretory vesicles and endolysosomal compartments. The majority of trafficking is from the Golgi to the endosomal compartment where sortilin deposits cargo targeted for catabolism in the lysosome and then is trafficked back to the Golgi via a retromer complex. At the cell surface, sortilin can remain intact and act as a receptor for extracellular ligands that can initiate signaling cascades or be internalized as a method of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Additionally, cell surface sortilin protein can undergo an additional cleavage that results in the release of the soluble form of the protein into the extracellular space. The sortilin receptor binds the nerve growth factor precursor (proNGF), neurotensin and Progranulin (PGRN), a secreted growth factor implicated in a multitude of processes ranging from regulation of inflammation to wound healing, tumorigenesis and neurological diseases. Sortilin controls PGRN trafficking and lysosomal degradation, but PGRN exerts its multiple functions independent of sortilin. Sortilin down-regulation via blocking antibodies, such as Latozinemab Biosimilar, is a key mechanism in increasing PGRN levels suggesting that sortilin is a potential target to correct PGRN reduction, such as that in patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) caused by GRN mutations.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161





![Sortilin 1 antibody [C1C3] detects Sortilin 1 protein by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV10 rat E18 primary cortical neurons were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Sortilin 1 protein stained by Sortilin 1 antibody [C1C3] (GTX110857) diluted at 1:500. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT1338] (GTX631831) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX110857/GTX110857_40051_20170824_IFA_w_23060500_433.webp)