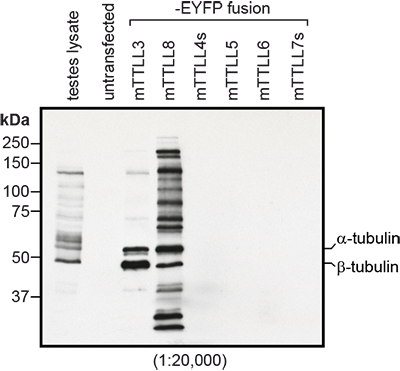
Immunoblot analysis of protein glycylation using anti-Tubulin (glycylated), pAb (Gly-pep1) (Prod. No. AG-25B-0034). Method: HEK-293T cells are grown in standard culture conditions, transfected with plasmids expressing the glycylases TTLL3 and TTLL8
anti-Tubulin (glycylated), pAb (Gly-pep1)
AG-25B-0034
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityCanine, Human, Mouse
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-Tubulin (glycylated), pAb (Gly-pep1)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- HostRabbit
- Scientific DescriptionMicrotubules are key cytoskeletal elements that are found in all eukaryotic cells. Microtubules fulfil a large range of different functions, which are thought to be controlled by the tubulin code - mechanism to generate distinct microtubule identities. One mechanism to label specific microtubules are tubulin posttranslational modifications (PTMs), of which a large variety exists. One of these modifications is glycylation, which is generated by the addition of secondary (branched) glycine chains to the main (primary) peptide chain of the protein. The length of these branch chains can vary from one to more than 20 glycine residues. Glycylation is catalysed by the enzymes TTLL3, TTLL8 and TTLL10 from the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) family. Especially TTLL3 and TTLL8 are essential for the initiation of the glycylation because the generate the nascent glycine chain. The Gly-pep1 antibody was raised against a peptide mimicking beta2-tubulin (TUBB2A) with a single glycine branch on E437. The antibody specifically detects glycylated tubulin, and also other yet unknown glycylation substrates in cells as well as in tissues. As glycylation of microtubules is particularly found in cilia and flagella, Gly-pep1 labels motile cilia as well as primary cilia (Gadadhar et al. 2017) - Polyclonal Antibody. This antibody recognizes mono or bi-glycylated Tubulins. The activity of glycylating enzymes (TTLL3 and TTLL8) in cultured cells leads mainly to the modification of alpha- and beta-tubulin, but also of other, yet unidentified protein substrates also detected by the antibody Gly-pep1. In immunofluorescence labeling, the antibody strongly labels glycylated microtubules. Source: Rabbit. Applications: ICC, IP, WB. Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. Microtubules are key cytoskeletal elements that are found in all eukaryotic cells. Microtubules fulfil a large range of different functions, which are thought to be controlled by the tubulin code - mechanism to generate distinct microtubule identities. One mechanism to label specific microtubules are tubulin posttranslational modifications (PTMs), of which a large variety exists. One of these modifications is glycylation, which is generated by the addition of secondary (branched) glycine chains to the main (primary) peptide chain of the protein. The length of these branch chains can vary from one to more than 20 glycine residues. Glycylation is catalysed by the enzymes TTLL3, TTLL8 and TTLL10 from the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) family. Especially TTLL3 and TTLL8 are essential for the initiation of the glycylation because the generate the nascent glycine chain. The Gly-pep1 antibody was raised against a peptide mimicking beta2-tubulin (TUBB2A) with a single glycine branch on E437. The antibody specifically detects glycylated tubulin, and also other yet unknown glycylation substrates in cells as well as in tissues. As glycyation of microtubules is particularly found in cilia and flagella, Gly-pep1 labels motile cilia as well as primary cilia.
- ReactivityCanine, Human, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

