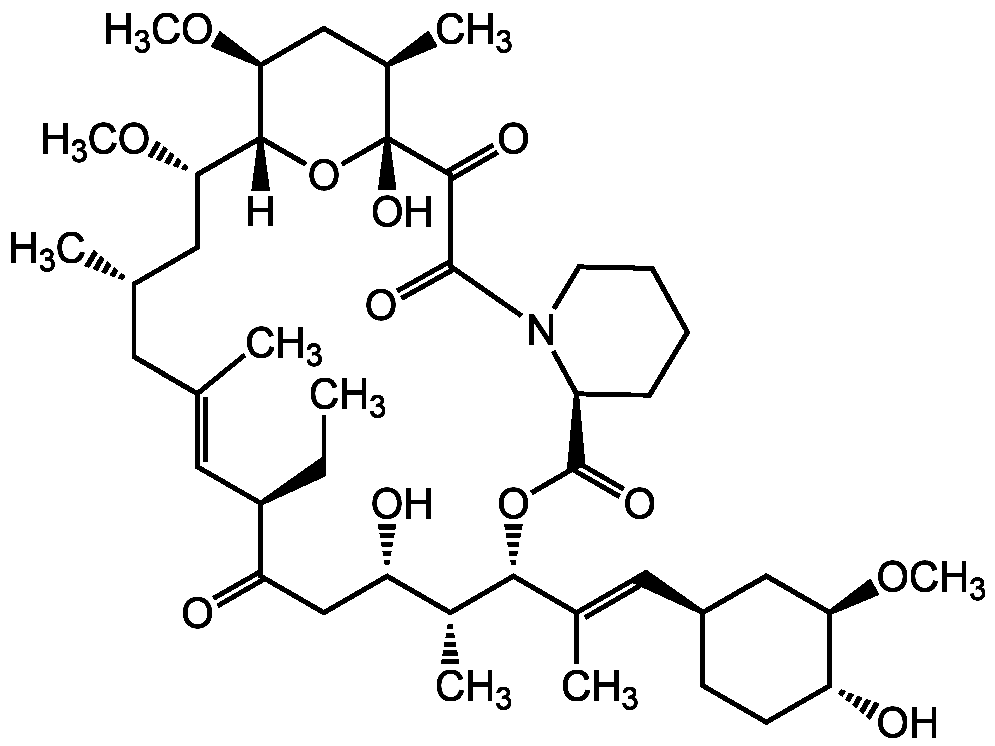
Chemical Structure
Ascomycin (high purity) [104987-12-4]

AG-CN2-0420
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAscomycin (high purity) [104987-12-4]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number104987-12-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC43H69NO12
- Molecular Weight792
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 104987-12-4. Formula: C43H69NO12. MW: 792. Isolated from Streptomyces sp. Macrolide antibiotic. Ethyl analog of FK506. Strong immunosuppressant. Binds to the FK-506-binding protein FKBP12. This complex inhibits calcineurin (protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B)). Suppresses the production of T helper type 1 (Th1) (interferon and IL-2) and Th2 (IL-4 and IL-10) cytokines in T lymphocytes and preferentially inhibits the activation of mast cells. Anti-inflammatory. Used for topical treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Potently inhibits anti-IgE-induced histamine and cytokine release and reduces IgE-dependent p38 MAPK activation in human basophils. Inhibits basophil degranulation at the initial phase of allergic skin reactions. Antifungal. Antimalaria compound. Anticonvulsant (antiepileptic). - Macrolide antibiotic. Ethyl analog of FK506 [1, 2]. Strong immunosuppressant. Binds to the FK-506-binding protein FKBP12. This complex inhibits calcineurin (protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B)) [2-4, 8]. Suppresses the production of T helper type 1 (Th1) (interferon and IL-2) and Th2 (IL-4 and IL-10) cytokines in T lymphocytes and preferentially inhibits the activation of mast cells [5-7]. Anti-inflammatory. Used for topical treatment of inflammatory skin diseases [5, 6]. Potently inhibits anti-IgE-induced histamine and cytokine release and reduces IgE-dependent p38 MAPK activation in human basophils. Inhibits basophil degranulation at the initial phase of allergic skin reactions [7, 8]. Antifungal [1]. Antimalaria compound [9]. Anticonvulsant (antiepileptic) [10, 11].
- SMILES[H][C@]12O[C@](O)([C@H](C)C[C@@H]1OC)C(=O)C(=O)N1CCCC[C@H]1C(=O)O[C@@H]([C@H](C)[C@@H](O)CC(=O)[C@H](CC)\C=C(C)\C[C@H](C)C[C@@H]2OC)C(\C)=C\[C@@H]1CC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C1)OC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Ascomycin, an antifungal antibiotic: T. Arai, et al.; J. Antibiot. 15, 231 (1962)
- Identity of immunosuppressant FR-900520 with ascomycin: M. Morisaki, et al.; J. Antibiot. 45, 126 (1992)
- Comparison of FK-506, rapamycin, ascomycin, and cyclosporine in mouse models of host-versus-graft disease and heterotopic heart transplantation: K.W. Mollison, et al.; Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 685, 55 (1993)
- FR-900520 and FR-900523, novel immunosuppressants isolated from a Streptomyces. II. Fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical and biological characteristics: H. Hatanaka, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 41, 1592 (1988)
- Ascomycins: promising agents for the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases: C. Paul, et al.; Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 9, 69 (2000)
- Ascomycin: an advance in the management of atopic dermatitis: C.E. Griffiths; Br. J. Dermatol. 144, 679 (2001)
- The ascomycin macrolactam pimecrolimus (Elidel, SDZ ASM 981) is a potent inhibitor of mediator release from human dermal mast cells and peripheral blood basophils: T. Zuberbier, et al.; J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108, 275 (2001)
- Calcineurin antagonists differentially affect mediator secretion, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinases from immunologically activated human basophils: K.E. Plath, et al.; Clin. Exp. Allergy 33, 342 (2003)
- Antimalarial effects of macrolactones related to FK520 (ascomycin) are independent of the immunosuppressive properties of the compounds: P. Monaghan, et al.; J. Infect. Dis. 191, 1342 (2005)
- Anticonvulsant effect of the calcineurin inhibitor ascomycin on seizures induced by picrotoxin microperfusion in the rat hippocampus: A. Vazquez-Lopez, et al.; Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 84, 511 (2006)
