Chemical Structure
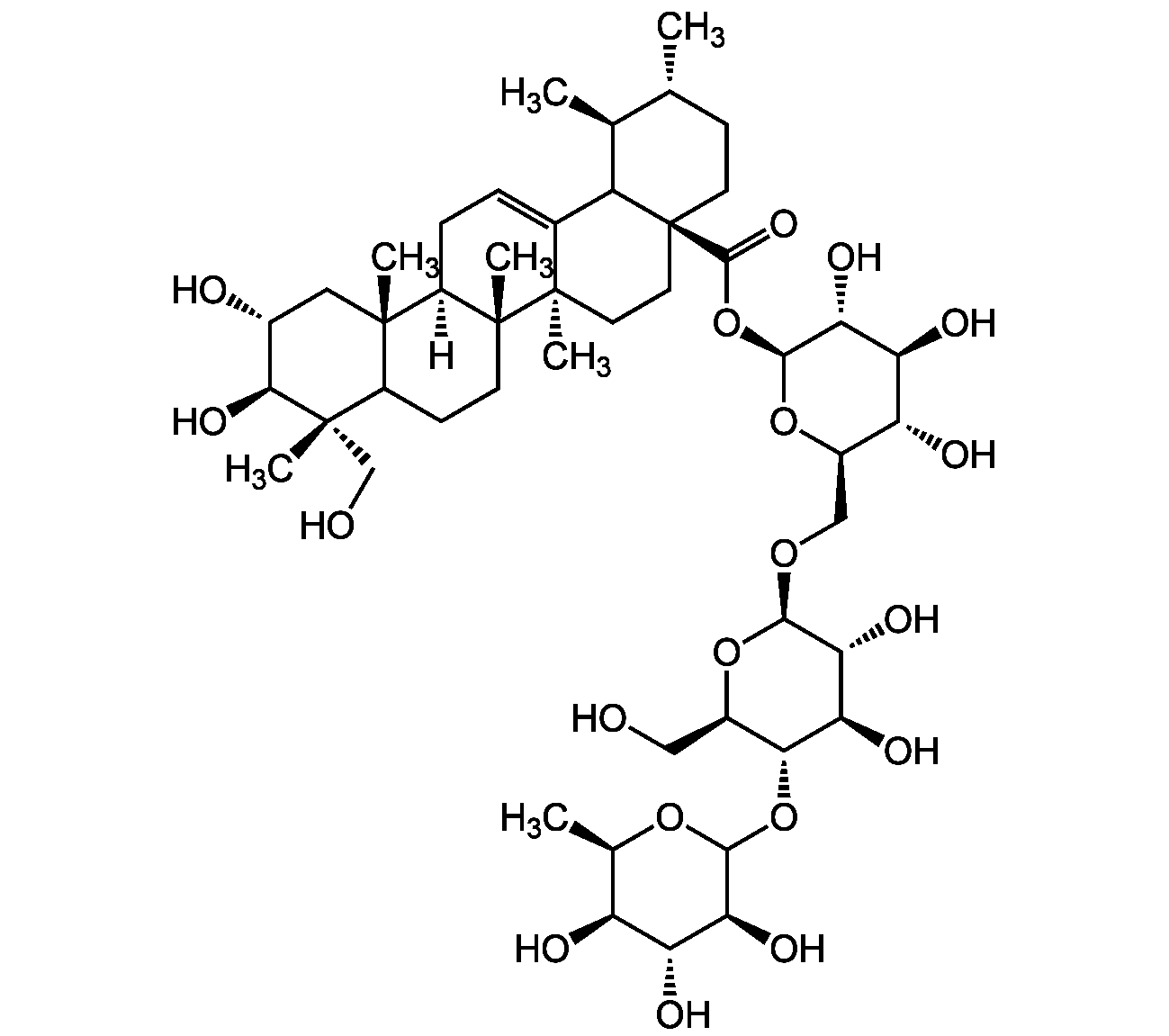
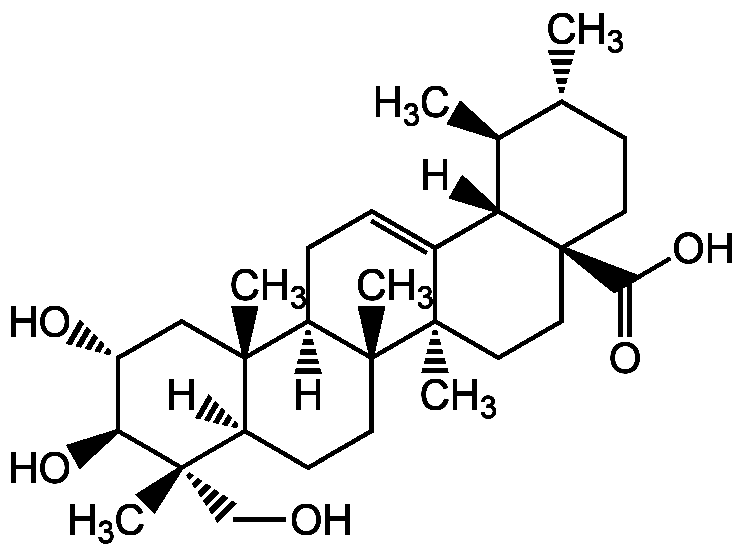
Asiatic acid [464-92-6] [464-92-6]
AG-CN2-0400
CAS Number464-92-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight488.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAsiatic acid [464-92-6] [464-92-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number464-92-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC30H48O5
- Molecular Weight488.7
- Scientific DescriptionApoptosis inducer [1, 3]. Cell cycle arrest inducer [1]. Anticancer compound [1, 5] Antioxidant. Hepatoprotective [2]. Inhibits TGF-beta/Smad-mediated fibrogenesis [12]. Stimulates wound healing [4]. Anti-diabetic. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor [6]. Neuroprotective [13]. Modulates multiple targets associated with amyloid-beta precursor protein processing and amyloid-beta protein clearance. Down regulates BACE1 and increases ADAM10 maturation [7]. Anti-hyperglycemic compound [8, 14]. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive compound [9]. Antiangiogenic [10]. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor [11]. PPARgamma inhibitor through a C/EBPbeta-independent mechanisms [15]. Anti-osteoporotic. Inhibits adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) [15]. - Chemical. CAS: 464-92-6. Formula: C30H48O5. MW: 488.7. Isolated from Centella asiatica. Apoptosis inducer. Cell cycle arrest inducer. Anticancer compound Antioxidant. Hepatoprotective. Inhibits TGF-beta/Smad-mediated fibrogenesis. Stimulates wound healing. Anti-diabetic. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor. Neuroprotective. Modulates multiple targets associated with amyloid-beta precursor protein processing and amyloid-beta protein clearance. Down regulates BACE1 and increases ADAM10 maturation. Anti-hyperglycemic compound. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive compound. Antiangiogenic. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. PPARgamma inhibitor through a C/EBPbeta-independent mechanisms. Anti-osteoporotic. Inhibits adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC).
- SMILES[H][C@@]12CC[C@]3(C)[C@]([H])(CC=C4[C@]5([H])[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)CC[C@@]5(CC[C@@]34C)C(O)=O)[C@@]1(C)C[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@]2(C)CO
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Asiatic acid [464-92-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/E4/CgoaEWayRVWEa77IAAAAADt_xfs975.png)