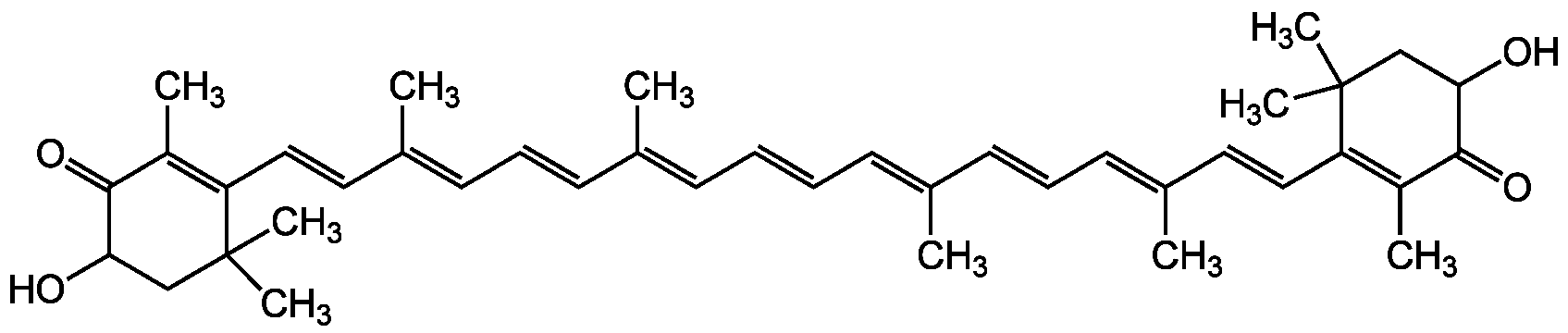
Chemical Structure
Astaxanthin [472-61-7] [472-61-7]
AG-CN2-0055
CAS Number472-61-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight596.8
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAstaxanthin [472-61-7] [472-61-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number472-61-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC40H52O4
- Molecular Weight596.8
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 472-61-7. Formula: C40H52O4. MW: 596.8. Synthetic. Potent antioxidant carotenoid. Free radical scavenger. Reduces oxidative stress. Anticancer compound. Anti-inflammatory. Blocks NF-kappaB activation. Anti-hypertensive. Cardiovascular protective. Improves neuronal stem cell potential. Neuroprotective. Inhibits tumor invasion. Apoptosis inducer . Increases insulin sensitivity. Attenuates diabetes associated coagulatory, oxidative and inflammatory stress. PPARalpha agonist and PPARgamma antagonist. Shows positive effects on obesity and insulin resistance Hepatoprotective. Reviews. - Potent antioxidant carotenoid [1]. Free radical scavenger [1, 3]. Reduces oxidative stress [1, 3]. Anticancer compound [2]. Anti-inflammatory. Blocks NF-kappaB activation [3, 18]. Anti-hypertensive. Cardiovascular protective [4, 6]. Improves neuronal stem cell potential [7, 9]. Neuroprotective [10]. Inhibits tumor invasion [11]. Apoptosis inducer [14]. Increases insulin sensitivity [12]. Attenuates diabetes associated coagulatory, oxidative and inflammatory stress [17]. PPARalpha agonist and PPARgamma antagonist [19, 20]. Shows positive effects on obesity and insulin resistance [17, 19, 20] Hepatoprotective [21]. Reviews [5, 6, 15, 16].
- SMILESC\C(\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)C(=O)C(O)CC1(C)C)=C/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C1=C(C)C(=O)C(O)CC1(C)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Astaxanthin [472-61-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/44/CgoaEGayGlKEXyJCAAAAAD8_tiA796.png)