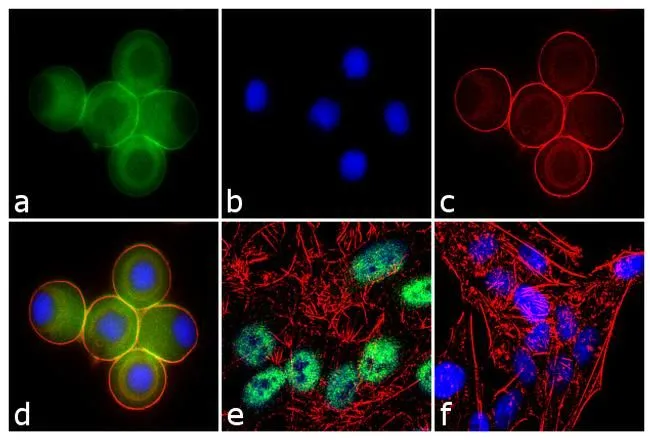
ICC/IF analysis of U-87 MG cells treated with 100 ng of Nocodazole for 16 hours using GTX11434 Ataxin 7 antibody. Panel e is untreated cell with nuclear localization. Panel f represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. Green : Primary antibody Blue : Nuclei Red : Actin Fixation : 4% paraformaldehyde Permeabilization : 0.1% Trito X-100 for 10 minutes Dilution: 2 microg/ml
Ataxin 7 antibody
GTX11434
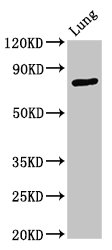
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityDrosophila, Human, Mouse, Rat
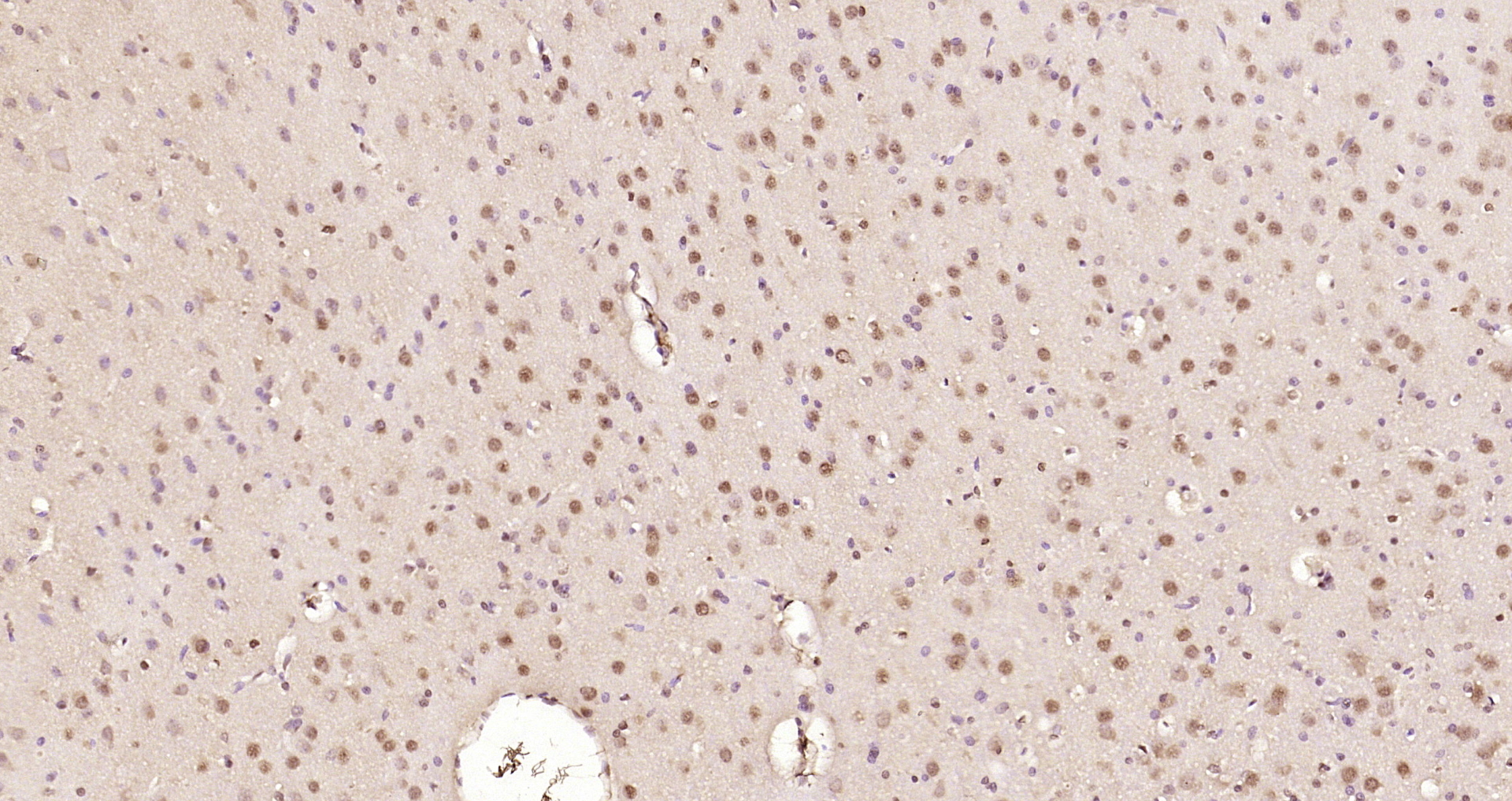
TargetATXN7
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAtaxin 7 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1 microg/ml. ICC/IF: 2 microg/ml. FACS: 3-5 microg/106 cells. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6314
- Target nameATXN7
- Target descriptionataxin 7
- Target synonymsADCAII, OPCA3, SCA7, SGF73, ataxin-7, Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia with retinal degeneration, SAGA associated factor 73 kDa homolog, spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO15265
- Protein NameAtaxin-7
- Scientific DescriptionThe autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxias (ADCA) are a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of the cerebellum, brain stem and spinal cord. Clinically, ADCA has been divided into three groups: ADCA types I-III. ADCAI is genetically heterogeneous, with five genetic loci, designated spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6, being assigned to five different chromosomes. ADCAII, which always presents with retinal degeneration (SCA7), and ADCAIII often referred to as the pure cerebellar syndrome (SCA5), are most likely homogeneous disorders. Several SCA genes have been cloned and shown to contain CAG repeats in their coding regions. ADCA is caused by the expansion of the CAG repeats, producing an elongated polyglutamine tract in the corresponding protein. The expanded repeats are variable in size and unstable, usually increasing in size when transmitted to successive generations. This locus has been mapped to chromosome 3, and it has been determined that the diseased allele associated with spinocerebellar ataxia-7 contains 37-306 CAG repeats (near the N-terminus), compared to 4-35 in the normal allele. The encoded protein is a component of the SPT3/TAF9/GCN5 acetyltransferase (STAGA) and TBP-free TAF-containing (TFTC) chromatin remodeling complexes, and it thus plays a role in transcriptional regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]
- ReactivityDrosophila, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203