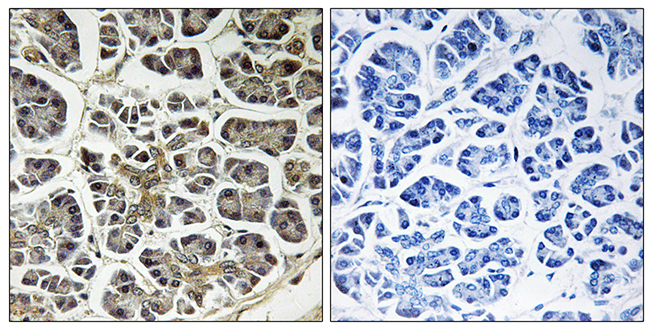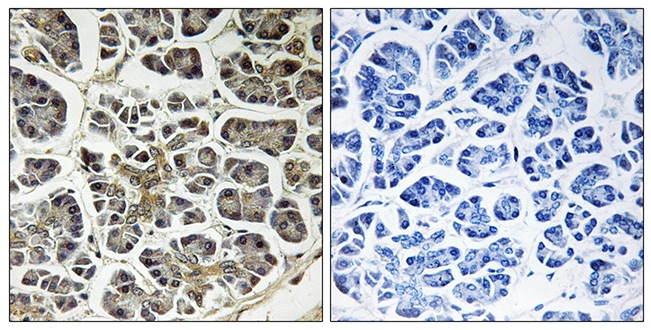
IHC-P analysis of human pancreas tissue using GTX87662 ATP5G2 antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
ATP5G2 antibody
GTX87662
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetATP5MC2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameATP5G2 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:50~1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID517
- Target nameATP5MC2
- Target descriptionATP synthase membrane subunit c locus 2
- Target synonymsATP5A, ATP5G2, ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C2, mitochondrial, ATP synthase c subunit, ATP synthase lipid-binding protein, mitochondrial, ATP synthase proteolipid P2, ATP synthase proton-transporting mitochondrial F(0) complex subunit C2, ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F0 complex, subunit C2 (subunit 9), ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial Fo complex subunit C2 (subunit 9), ATPase protein 9, ATPase subunit C, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD)-reactive proteolipid subunit
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ06055
- Protein NameATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C2, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and single representatives of the gamma, delta, and epsilon subunits. The proton channel likely has nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). There are three separate genes which encode subunit c of the proton channel and they specify precursors with different import sequences but identical mature proteins. The protein encoded by this gene is one of three precursors of subunit c. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2018]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161