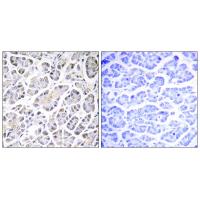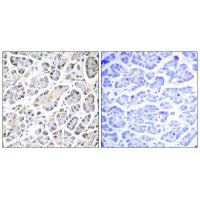
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human pancreas tissue using ATP5G3 antibody.
ATP5G3 Antibody
CSB-PA783665
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetATP5MC3
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameATP5G3 Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID518
- Target nameATP5MC3
- Target descriptionATP synthase membrane subunit c locus 3
- Target synonymsATP5G3, DYTSPG, P3, ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C3, mitochondrial, ATP synthase lipid-binding protein, mitochondrial, ATP synthase proteolipid P3, ATP synthase proton-transporting mitochondrial F(0) complex subunit C3, ATP synthase subunit 9, ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F0 complex, subunit C3 (subunit 9), ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial Fo complex subunit C3 (subunit 9), ATP synthase, mitochondrial, C subunit-3, ATPase protein 9, ATPase subunit C, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD)-reactive proteolipid subunit
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP48201
- Protein NameATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C3, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionMitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F1F0 ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F1 - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F0 - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F1 is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F0 domain. A homomeric c-ring of probably 10 subunits is part of the complex rotary element. HAMAP-Rule MF_01396 Yan W.L., Genomics 24:375-377(1994). L., Du H., Nature 434:724-731(2005). The MGC Project Team; Genome Res. 14:2121-2127(2004).
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161