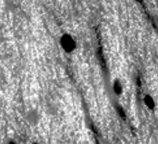
Immunohistochemistry analysis of bassoon localization in the rat brain cerebellar molecular layer using Bassoon, mAb (SAP7F407)
Bassoon antibody [SAP7F407]
GTX13249
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetBsn
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameBassoon antibody [SAP7F407]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:1000. IP: 2.5microg. IHC: 1:400. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDSAP7F407
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID29138
- Target nameBsn
- Target descriptionbassoon (presynaptic cytomatrix protein)
- Target synonymsneuronal double zinc finger protein; protein bassoon; zinc finger protein 231; Znf231
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Scientific DescriptionBassoon is a 420 kDa protein that is a localized at the presynaptic nerve terminals and is believed to play a role in the structural and functional organization of the synaptic vesicle cycle. Bassoon does not belong to any known protein families. It has been found in rat and mouse with sequence identity of the two proteins at 96%. The human BASSOON gene has recently been cloned and localized. Bassoon is predicted to contain two double-zinc fingers, three coiled-coil regions, and two polyglutamine domains. The polyglutamine domains in the C-terminus are of interest, since it is known that for some human proteins, such as Huntingtin, abnormal amplification of this region can cause late-onset neurodegeneration. Bassoon is concentrated at sites opposite to postsynaptic densities in synaptic terminals and in cultured neurons, it is found to colocalize with GABA (A) and glutamate (GluR1) receptors.Another presynaptic protein, Piccolo was found to colocalize with Bassoon in cultured hippocampal neurons. These observations suggested that they serve specific functions at synaptic junctions and may be involved in organization of the cytoskeleton at the site of neurotransmitter release.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Exacerbated response to oxidative stress in the Retinitis Pigmentosa Cerkl(KD/KO) mouse model triggers retinal degeneration pathways upon acute light stress.Read more
- Multiple roles of integrin-alpha3 at the neuromuscular junction. Ross JA et al., 2017 May 15, J Cell SciRead more
- Postsynaptic Y654 dephosphorylation of beta-catenin modulates presynaptic vesicle turnover through increased n-cadherin-mediated transsynaptic signaling. Chen CY et al., 2017 Jan, Dev NeurobiolRead more
- mSYD1A, a mammalian synapse-defective-1 protein, regulates synaptogenic signaling and vesicle docking. Wentzel C et al., 2013 Jun 19, NeuronRead more
- Transgenic strategy for identifying synaptic connections in mice by fluorescence complementation (GRASP). Yamagata M et al., 2012, Front Mol NeurosciRead more
- Distribution of vesicular glutamate transporters in rat and human retina. Gong J et al., 2006 Apr 12, Brain ResRead more

![Western blot analysis of rat brain tissue lysate using Bassoon antibody [SAP7F407]. Western blot analysis of rat brain tissue lysate using Bassoon antibody [SAP7F407].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX13249/Bassoon-antibody-SAP7F407_WB_GTX13249-1_w_23060523_753.webp)