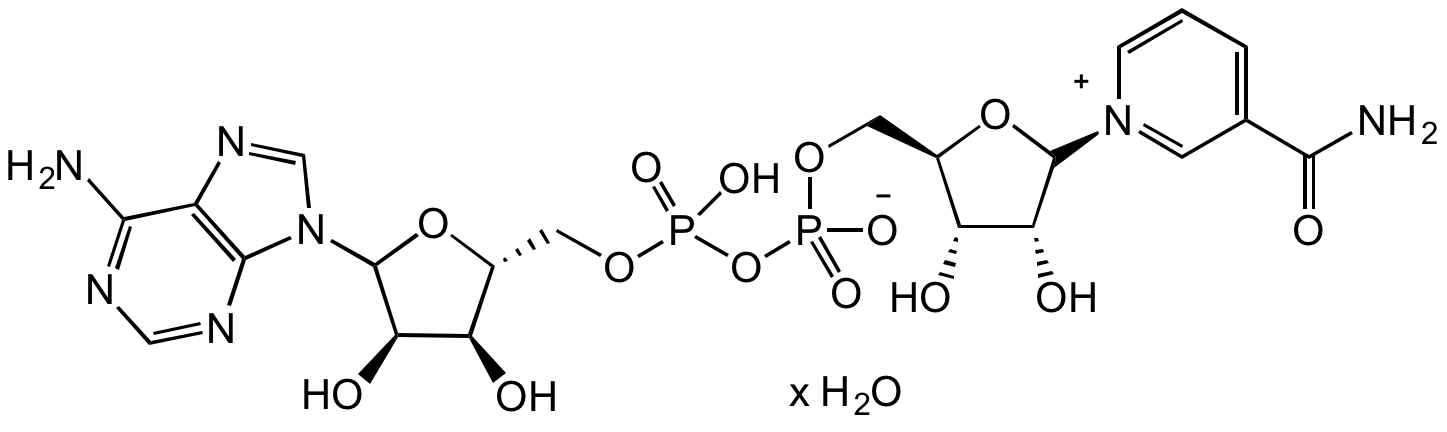
Chemical Structure
beta-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrate [53-84-9]
CDX-N0222
CAS Number53-84-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight663.43 (anhydrous basis)
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product Namebeta-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrate [53-84-9]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number53-84-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC21H27N7O14P2 . xH2O
- Molecular Weight663.43 (anhydrous basis)
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 53-84-9. Formula: C21H27N7O14P2 . xH2O. MW: 663.43 (anhydrous basis). NAD+, known more formally as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a signaling molecule as well as a cofactor or substrate for many enzymes. It acts as an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules while being converted to its reduced form, NADH. NAD+ is also essential for the activity of several enzymes, including poly(ADP)-ribose polymerases and cADP-ribose synthases. For example, it is used by some sirtuins to mediate protein deacetylation, producing O-acetyl-ADP-ribose and nicotinamide as well as the deacetylated protein. NAD+ is an important player and factor to research metabolic pathways and pathologies. - NAD+, known more formally as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a signaling molecule as well as a cofactor or substrate for many enzymes. It acts as an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules while being converted to its reduced form, NADH. NAD+ is also essential for the activity of several enzymes, including poly(ADP)-ribose polymerases and cADP-ribose synthases. For example, it is used by some sirtuins to mediate protein deacetylation, producing O-acetyl-ADP-ribose and nicotinamide as well as the deacetylated protein. NAD+ is an important player and factor to research metabolic pathways and pathologies.
- SMILESO[C@H]1C(N2C=NC3=C2N=CN=C3N)O[C@H](COP(O)(OP(OC[C@@H]4[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]([N+]5=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C5)O4)([O-])=O)=O)[C@H]1O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![NAD+ [53-84-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/37/2C/CgoaEGaySRKEXk-xAAAAALrZH3s634.png)