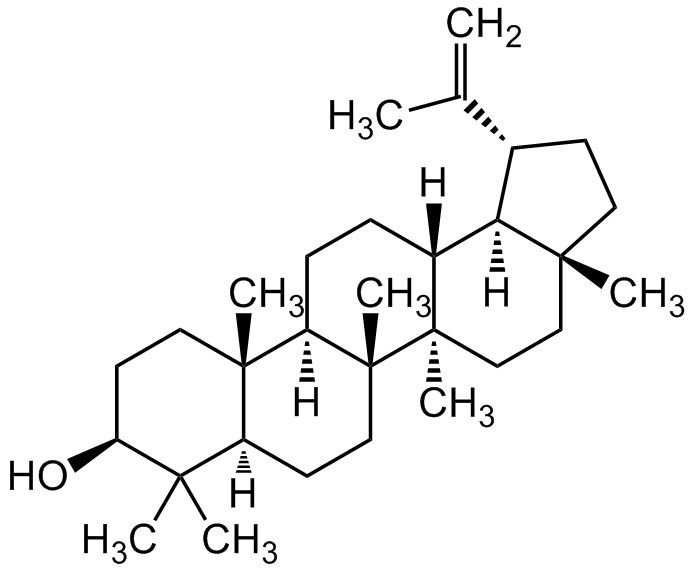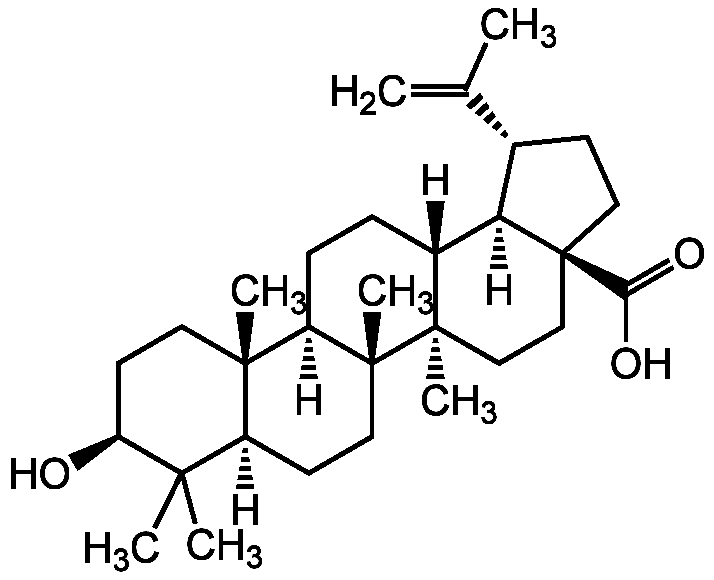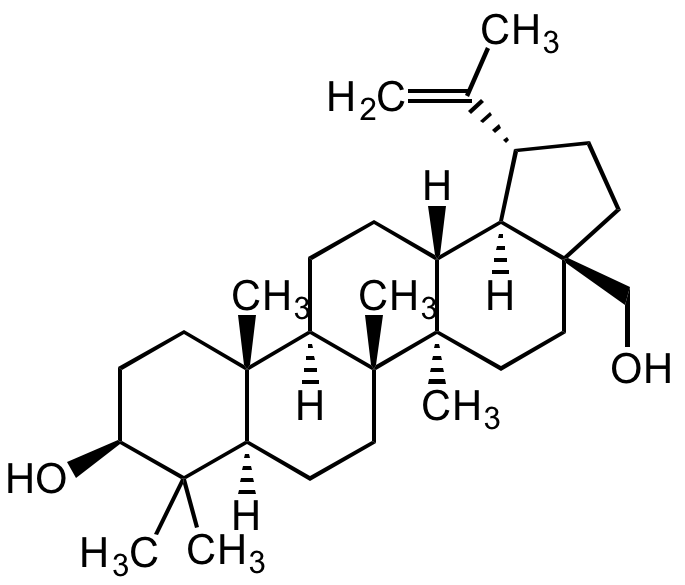
Chemical Structure
Betulin
AG-CN2-0476
CAS Number473-98-3
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight442.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameBetulin
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number473-98-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC30H50O2
- Molecular Weight442.7
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 473-98-3. Formula: C30H50O2. MW: 442.7. Isolated from Betulaceae family tree bark. Specific SREBPs (sterol regulatory element-binding proteins) inhibitor. Inhibits ER-Golgi translocation of SREBPs through binding to SCAP in an INSIG-dependent manner. Improves hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduces atherosclerotic plaques. Lowers cholesterol levels through inhibition of SREBP-2 activation. Reduces weight gain and adipose tissue size in vivo. Increases oxygen consumption and energy expenditure. Increases UCP1/2 levels in brown adipose tissue (BAT) after cold stimulation. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer. DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory compound. Shown to inhibit LPS-induced NO production through the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Antiviral compound. - Specific SREBPs (sterol regulatory element-binding proteins) inhibitor. Inhibits ER-Golgi translocation of SREBPs through binding to SCAP in an INSIG-dependent manner. Improves hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduces atherosclerotic plaques. Lowers cholesterol levels through inhibition of SREBP-2 activation. Reduces weight gain and adipose tissue size in vivo. Increases oxygen consumption and energy expenditure. Increases UCP1/2 levels in brown adipose tissue (BAT) after cold stimulation. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer. DNA topoisomerase II inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory compound. Shown to inhibit LPS-induced NO production through the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Antiviral compound.
- SMILES[H][C@]12[C@@H](CC[C@]1(CO)CC[C@]1(C)[C@]2([H])CC[C@]2([H])[C@@]3(C)CC[C@H](O)C(C)(C)[C@]3([H])CC[C@@]12C)C(C)=C
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200