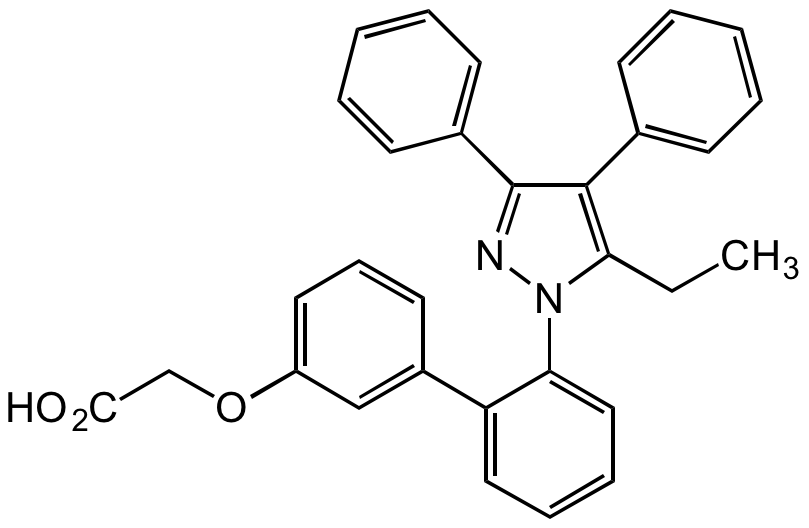
Chemical Structure
BMS-309403 [300657-03-8]
AG-CR1-3640
CAS Number300657-03-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight474.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameBMS-309403 [300657-03-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number300657-03-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC31H26N2O3
- Molecular Weight474.6
- Scientific DescriptionCell permeable, potent and selective fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4; A-FABP; ALBP; adipocyteP2 protein) inhibitor that competitively targets the fatty acid-binding pocket (Ki= <2nM). Inhibits FABP3 (muscle) and FABP5 (epidermal) with lower affinity (Ki=250nM and 350nM, respectively). FABP4 is an intracellular lipid-binding protein responsible for the transportation of fatty acids. It is expressed primarily in adipose tissue and is associated with inflammation, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Glucose uptake stimulator. Reduces blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity in a mouse model of obesity. Protects against the development of insulin resistance associated with genetic or diet-induced obesity in mice. Anti-atherosclerotic. Decreases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes in vitro and reduces atherosclerotic lesion area in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. - Chemical. CAS: 300657-03-8. Formula: C31H26N2O3. MW: 474.6. Cell permeable, potent and selective fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4; A-FABP; ALBP; adipocyteP2 protein) inhibitor that competitively targets the fatty acid-binding pocket (Ki= <2nM). Inhibits FABP3 (muscle) and FABP5 (epidermal) with lower affinity (Ki=250nM and 350nM, respectively). FABP4 is an intracellular lipid-binding protein responsible for the transportation of fatty acids. It is expressed primarily in adipose tissue and is associated with inflammation, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Glucose uptake stimulator. Reduces blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity in a mouse model of obesity. Protects against the development of insulin resistance associated with genetic or diet-induced obesity in mice. Anti-atherosclerotic. Decreases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes in vitro and reduces atherosclerotic lesion area in a mouse model of atherosclerosis.
- SMILESCCC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)=NN1C4=CC=CC=C4C5=CC(OCC(O)=O)=CC=C5
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![BMS-309403 [300657-03-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/C3/CgoaEGayKvmEPRpQAAAAAIAmwGs883.png)