Chemical Structure
PS-341 [Bortezomib] [179324-69-7]

AG-CR1-3602
CAS Number179324-69-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight384.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameBortezomib [179324-69-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ADR Class6.1
- CAS Number179324-69-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
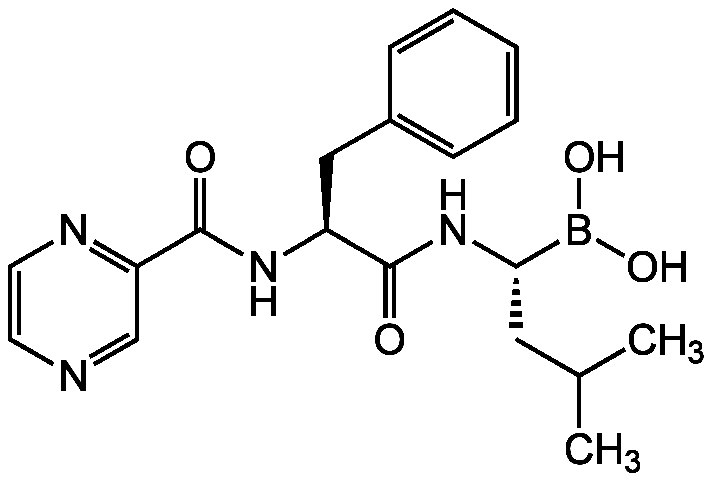
- Molecular FormulaC19H25BN4O4
- Molecular Weight384.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 179324-69-7. Formula: C19H25BN4O4. MW: 384.2. Highly potent, selective and reversible cell permeable inhibitor of the proteasome. Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like peptidase activity of the proteasome. Calpain and cathepsin inhibitor. Autophagy activator. Anticancer compound. Inhibits proliferation and migration of several tumor cell lines with nanomolar potency. Apoptosis inducer. - Highly potent, selective and reversible cell permeable inhibitor of the proteasome. Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like and caspase-like peptidase activity of the proteasome. Calpain and cathepsin inhibitor. Autophagy activator. Anticancer compound. Inhibits proliferation and migration of several tumor cell lines with nanomolar potency. Apoptosis inducer.
- SMILESCC(C)C[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C1=NC=CN=C1)B(O)O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UN NumberUN3249
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents: J. Adams, et al.; Cancer Res. 59, 2615 (1999)
- Development of the proteasome inhibitor Velcade (Bortezomib): J. Adams & M. Kauffmann; Cancer Invest. 22, 304 (2004)
- Bortezomib inhibits PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase and induces apoptosis via ER stress in human pancreatic cancer cells: S.T. Nawrocki, et al.; Cancer Res. 65, 11510 (2005)
- A novel orally active proteasome inhibitor induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells with mechanisms distinct from Bortezomib: D. Chauhan, et al.; Cancer Cell 8, 407 (2005)
- Importance of the different proteolytic sites of the proteasome and the efficacy of inhibitors varies with the protein substrate: A.F. Kisselev, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 8582 (2006)
- Bortezomib interactions with chemotherapy agents in acute leukemia in vitro: T.M. Horton, et al.; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 58, 13 (2006)
- Bortezomib as an antitumor agent: A.M. Roccaro, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 7, 441 (2006) (Review)
- Aggravated endoplasmic reticulum stress as a basis for enhanced glioblastoma cell killing by bortezomib in combination with celecoxib or its non-coxib analogue, 2,5-dimethyl-celecoxib: A. Kardosh, et al.; Cancer Res. 68, 843 (2008)
- Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib) induces calpain-dependent IkappaB(alpha) degradation: C. Li, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 16096 (2010)
- Bortezomib suppresses function and survival of plasmacytoid dendritic cells by targeting intracellular trafficking of Toll-like receptors and endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis: M. Hirai, et al.; Blood 117, 500 (2011)
