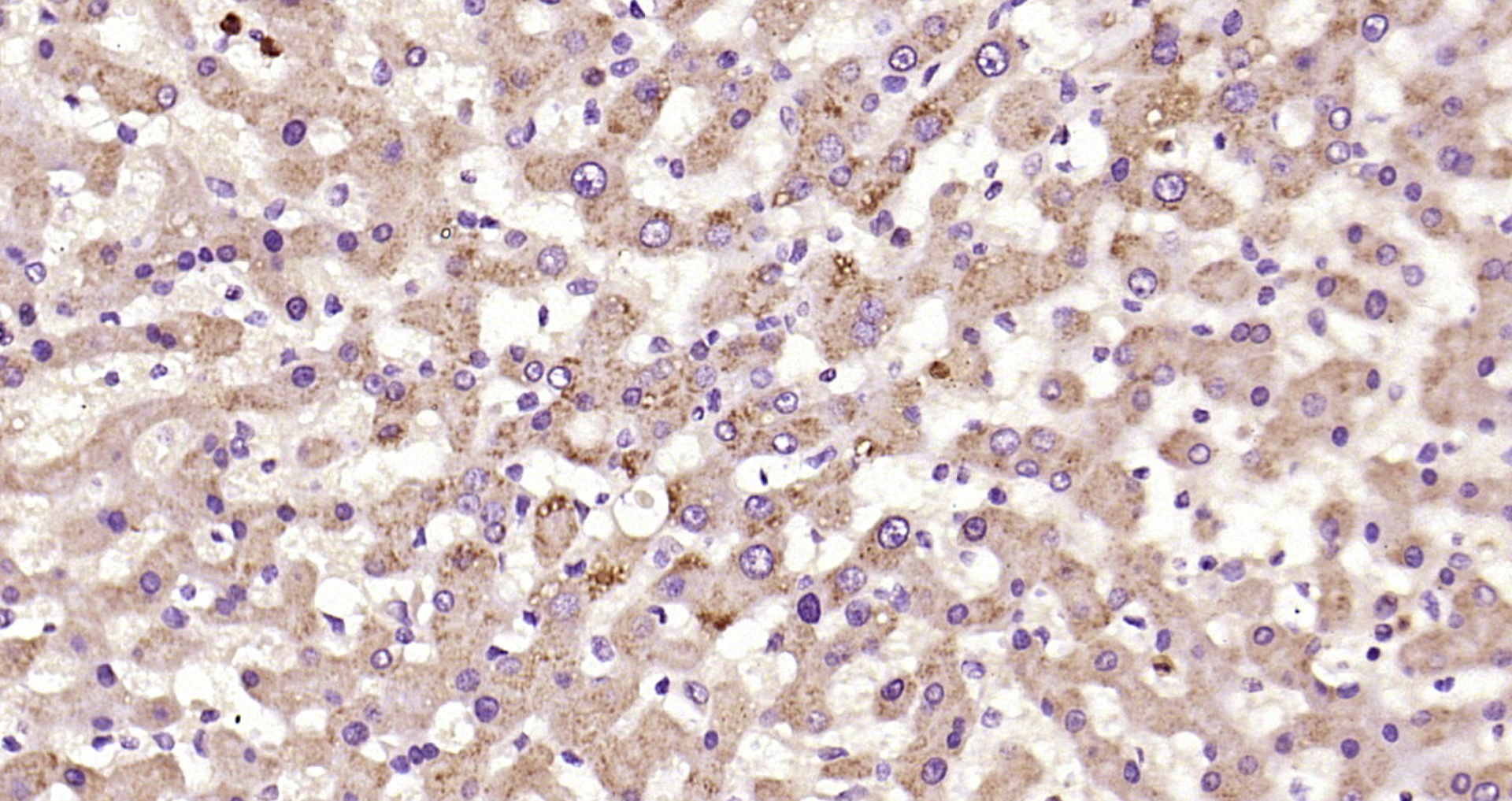
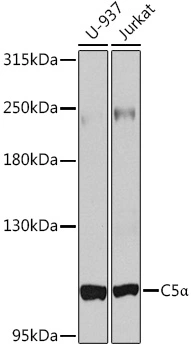
C5 / C5a antibody [561]
GTX54438
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameC5 / C5a antibody [561]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier Note*Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID561
- Concentration100 ug/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID727
- Target nameC5
- Target descriptioncomplement C5
- Target synonymsanaphylatoxin C5a analog; C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 4; C5a; C5a anaphylatoxin; C5b; C5D; complement C5; complement component 5; CPAMD4; ECLZB; prepro-C5
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP01031
- Protein NameComplement C5
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a component of the complement system, a part of the innate immune system that plays an important role in inflammation, host homeostasis, and host defense against pathogens. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate multiple protein products, including the C5 alpha chain, C5 beta chain, C5a anaphylatoxin and C5b. The C5 protein is comprised of the C5 alpha and beta chains, which are linked by a disulfide bridge. Cleavage of the alpha chain by a convertase enzyme results in the formation of the C5a anaphylatoxin, which possesses potent spasmogenic and chemotactic activity, and the C5b macromolecular cleavage product, a subunit of the membrane attack complex (MAC). Mutations in this gene cause complement component 5 deficiency, a disease characterized by recurrent bacterial infections. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203