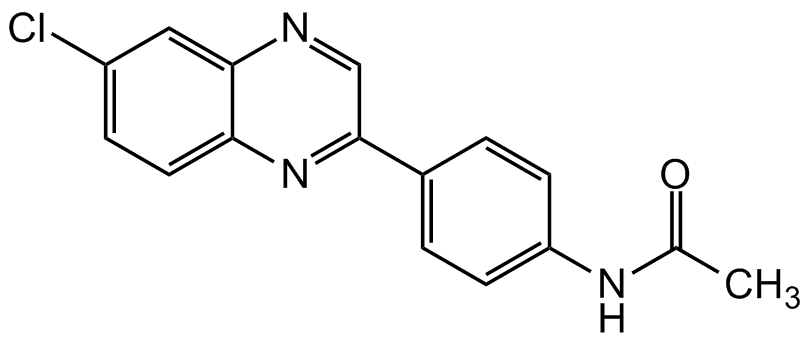
Chemical Structure
CA77.1 [CMA Activator]

AG-CR1-0165
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCA77.1
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number2412270-22-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC16H12ClN3O
- Molecular Weight297.7
- Scientific DescriptionCA77.1 is a novel selective chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) activator by increasing the expression of the lysosomal receptor for this pathway, LAMP2A, in lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), is a selective autophagy shown to degrade neurodegeneration-related proteins such as alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) or tau. Loss of neuronal CMA leads to altered neuronal function, selective changes in the neuronal metastable proteome and proteotoxicity. Chemical upregulation of CMA has been shown to ameliorate pathology in AD experimental mouse models, reduce brain pathology and improve disease phenotype. CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vitro and in vivo (in contrary to its derivative AR7 which was not suitable for in vivo application). CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vivo, and demonstrates brain penetrance and favorable pharmacokinetics. It has been shown in animal studies that administration of CA77.1 to enhance chaperone-mediated autophagy, may help to degrade toxic pathogenic protein products such as tau proteins and has potential applications in the treatment of Alzheimers disease. - Chemical. CAS: 2412270-22-3. Formula: C16H12ClN3O. MW: 297.7. CA77.1 is a novel selective chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) activator by increasing the expression of the lysosomal receptor for this pathway, LAMP2A, in lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), is a selective autophagy shown to degrade neurodegeneration-related proteins such as alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) or tau. Loss of neuronal CMA leads to altered neuronal function, selective changes in the neuronal metastable proteome and proteotoxicity. Chemical upregulation of CMA has been shown to ameliorate pathology in AD experimental mouse models, reduce brain pathology and improve disease phenotype. CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vitro and in vivo (in contrary to its derivative AR7 which was not suitable for in vivo application). CA77.1 is able to activate CMA in vivo, and demonstrates brain penetrance and favorable pharmacokinetics. It has been shown in animal studies that administration of CA77.1 to enhance chaperone-mediated autophagy, may help to degrade toxic pathogenic protein products such as tau proteins and has potential applications in the treatment of Alzheimers disease.
- SMILESClC1=CC=C(N=C(C2=CC=C(NC(C)=O)C=C2)C=N3)C3=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
