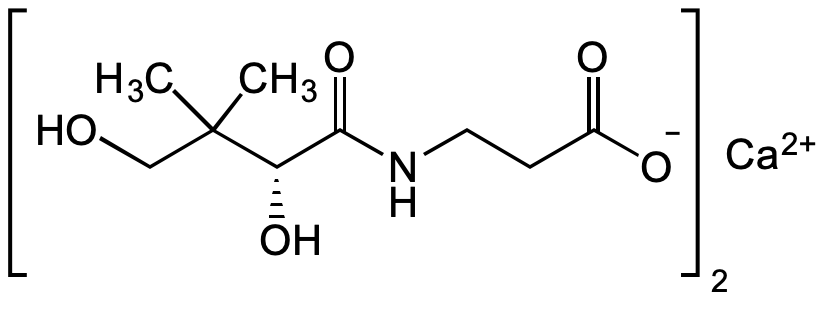
Chemical Structure
Calcium pantothenate [137-08-6] [137-08-6]
CDX-C0657
CAS Number137-08-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight238.27
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameCalcium pantothenate [137-08-6] [137-08-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number137-08-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC9H16NO5 . 0.5Ca
- Molecular Weight238.27
- Scientific DescriptionCalcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) is a water-soluble vitamin, an essential nutrient required to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and fats. CoA is important in energy metabolism for pyruvate to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) as acetyl-CoA, and for alpha-ketoglutarate to be transformed to succinyl-CoA in the cycle. CoA is also important in the biosynthesis of many important compounds such as fatty acids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine. CoA is incidentally also required in the formation of ACP, which is also required for fatty acid synthesis in addition to CoA. Small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food, with high amounts in whole-grain cereals, legumes, eggs, meat, royal jelly, avocado and yogurt. Only the dextrorotatory (D) isomer possesses biological activity, such as antibacterial or metabolic properties. - Chemical. CAS: 137-08-6. Formula: C9H16NO5 . 0.5Ca. MW: 238.27. Synthetic. Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) is a water-soluble vitamin, an essential nutrient required to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and fats. CoA is important in energy metabolism for pyruvate to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) as acetyl-CoA, and for alpha-ketoglutarate to be transformed to succinyl-CoA in the cycle. CoA is also important in the biosynthesis of many important compounds such as fatty acids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine. CoA is incidentally also required in the formation of ACP, which is also required for fatty acid synthesis in addition to CoA. Small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food, with high amounts in whole-grain cereals, legumes, eggs, meat, royal jelly, avocado and yogurt. Only the dextrorotatory (D) isomer possesses biological activity, such as antibacterial or metabolic properties.
- SMILESOCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(NCCC([O-])=O)=O.[Ca+2]
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![D-Pantothenic acid hemicalcium salt [137-08-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/7A/CgoaEWY7Lv6EfUoVAAAAAPIHqRQ960.png)