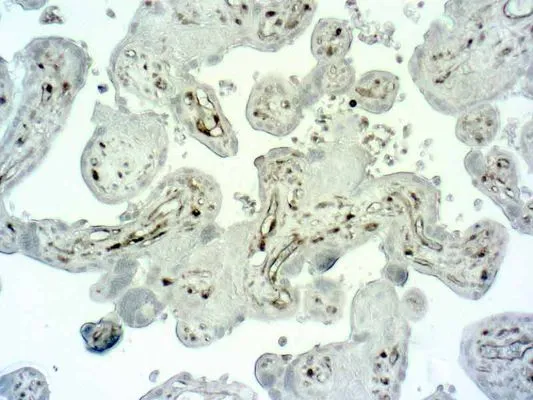
IHC-P analysis of human placenta tissue section using GTX03342 Caspase 1 antibody.
Caspase 1 antibody
GTX03342
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCASP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCaspase 1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:50-1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID834
- Target nameCASP1
- Target descriptioncaspase 1
- Target synonymsCASP1 nirs variant 1; caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase; caspase-1; caspase-1 isoform alpha; ICE; IL-1 beta-converting enzyme; IL1BC; IL1B-convertase; interleukin 1, beta, convertase; interleukin 1-B converting enzyme; P45
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP29466
- Protein NameCaspase-1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a protein which is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce 2 subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This gene was identified by its ability to proteolytically cleave and activate the inactive precursor of interleukin-1, a cytokine involved in the processes such as inflammation, septic shock, and wound healing. This gene has been shown to induce cell apoptosis and may function in various developmental stages. Studies of a similar gene in mouse suggest a role in the pathogenesis of Huntington disease. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
