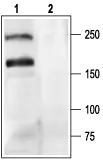
WB analysis of rat brain membrane lysate using GTX54753 Cav2.1 antibody preincubated with or without immunogen peptide. Dilution : 1:200
Cav2.1 antibody
GTX54753
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCacna1a
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCav2.1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.8 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID25398
- Target nameCacna1a
- Target descriptioncalcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 A
- Target synonymsBccA1, Cav2.1, rbA-1, voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A, BI, RBA-I, brain calcium channel 1, brain calcium channel I, brain class A, calcium channel alpha 1A, calcium channel, L type, alpha-1 polypeptide, calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit, calcium channel, voltage-dependent, alpha 1A subunit, voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav2.1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP54282
- Protein NameVoltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A
- Scientific Descriptionvoltage-gated calcium channel that may be involved in secretion coupling in pancreatic beta cells [RGD, Feb 2006]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Pain induces stable, active microcircuits in the somatosensory cortex that provide a therapeutic target. Okada T et al., 2021 Mar, Sci AdvRead this paper