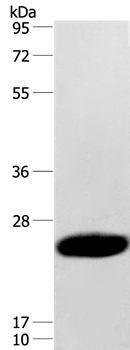
![Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Caveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX109650) diluted at 1:1000. Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Caveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX109650) diluted at 1:1000.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX109650/GTX109650_40009_20160121_WB_R_muscle_w_23060500_715.webp)
Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Caveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX109650) diluted at 1:1000.
Caveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term
GTX109650
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCAV3
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCaveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:20000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID859
- Target nameCAV3
- Target descriptioncaveolin 3
- Target synonymsLGMD1C, LQT9, MPDT, RMD2, VIP-21, VIP21, caveolin-3, M-caveolin, cavolin 3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP56539
- Protein NameCaveolin-3
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a caveolin family member, which functions as a component of the caveolae plasma membranes found in most cell types. Caveolin proteins are proposed to be scaffolding proteins for organizing and concentrating certain caveolin-interacting molecules. Mutations identified in this gene lead to interference with protein oligomerization or intra-cellular routing, disrupting caveolae formation and resulting in Limb-Girdle muscular dystrophy type-1C (LGMD-1C), hyperCKemia or rippling muscle disease (RMD). Alternative splicing has been identified for this locus, with inclusion or exclusion of a differentially spliced intron. In addition, transcripts utilize multiple polyA sites and contain two potential translation initiation sites. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Caveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX109650) diluted at 1:1000. Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Caveolin 3 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX109650) diluted at 1:1000.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX109650/GTX109650_40009_20160121_WB_M_muscle_w_23060500_880.webp)