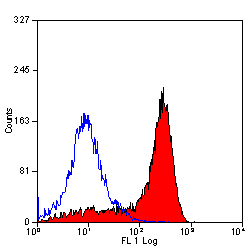
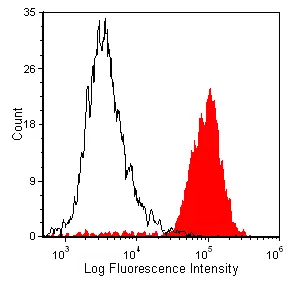
CD11b antibody [OX-42] (PE)
GTX76061
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityRat
TargetItgam
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD11b antibody [OX-42] (PE)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteOptimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDOX-42
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateRPE
- Gene ID25021
- Target nameItgam
- Target descriptionintegrin subunit alpha M
- Target synonymsCd11b, integrin alpha-M, integrin, alpha M
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Scientific DescriptionRecognises most macrophages (including resident peritoneal and activated macrophages), Kupffer cells, but only about 35% alveolar macrophages. The MRC OX-42 antibody also labels dendritic cells extensively, granulocytes and cells with the morphology of microglia in brain. MRC OX-42 precipitates three polypeptides of M.W 160,000, 103,000 and 95,000. The antibody inhibits complement mediated rosettes and is probably the rat equivalent of the human receptor for iC3b called CR3.
- ReactivityRat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Li S, Huang C, Tu C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes shuttling miR-150-5p alleviates mechanical allodynia in rats by targeting NOTCH2 in microglia. Mol Med. 2022,28(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00561-xRead this paper
- Truzzi F, Tibaldi C, Whittaker A, et al. Pro-Inflammatory Effect of Gliadins and Glutenins Extracted from Different Wheat Cultivars on an In Vitro 3D Intestinal Epithelium Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2020,22(1). doi: 10.3390/ijms22010172Read this paper
- Aminzadeh A, Tekiyeh Maroof N, Mehrabani M, et al. Investigating The Alterations of Oxidative Stress Status, Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms, MAP Kinase and Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway in Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from STZ Diabetic Rats. Cell J. 2020,22(Suppl 1):38-48. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2020.6958Read this paper
- Bai N, Zhang Q, Zhang W, et al. G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor activation upregulates interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in the hippocampus after global cerebral ischemia: implications for neuronal self-defense. J Neuroinflammation. 2020,17(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1715-xRead this paper
- Lin CH, Liao LY, Yang TY, et al. Microglia-Derived Adiposomes are Potential Targets for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019,39(5):591-604. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00665-9Read this paper
- Bonfante R, Napimoga MH, Macedo CG, et al. The P2X7 Receptor, Cathepsin S and Fractalkine in the Trigeminal Subnucleus Caudalis Signal Persistent Hypernociception in Temporomandibular Rat Joints. Neuroscience. 2018,391:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.09.005Read this paper
- Lin CH, Wang CH, Hsu SL, et al. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Neuron-Derived Conditioned Medium (NCM)-Mediated Protection of Ischemic Brain. PLoS One. 2016,11(1):e0146692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146692Read this paper
- Nakajima H, Uchida K, Guerrero AR, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes an alternative pathway of macrophage activation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012,29(8):1614-25. doi: 10.1089/neu.2011.2109Read this paper
- Takahashi K, Watanabe M, Suekawa Y, et al. IL-1beta in the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis contributes to extra-territorial allodynia/hyperalgesia following a trigeminal nerve injury. Eur J Pain. 2011,15(5):467.e1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.10.006Read this paper
- Zhao Z, Li Q, Hu J, et al. Lactosyl derivatives function in a rat model of severe burn shock by acting as antagonists against CD11b of integrin on leukocytes. Glycoconj J. 2009,26(2):173-88. doi: 10.1007/s10719-008-9174-0Read this paper