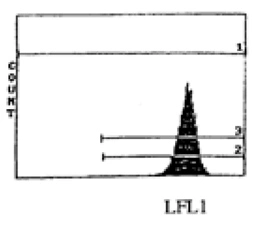
Staining of rat peritoneal macrophages using CD11b: FITC antibody (GTX21212) and FITC mouse IgG2a isotype control
CD11b/c equivalent antibody [OX 42] (FITC)
GTX21212
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityRat
TargetItgam
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD11b/c equivalent antibody [OX 42] (FITC)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteFACS: Use at a dilution of 1/1 - 1/20 (10microl/10^6cells). IHC-P: Use at a dilution of 1/1 - 1/20. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDOX 42
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateFITC
- Gene ID25021
- Target nameItgam
- Target descriptionintegrin subunit alpha M
- Target synonymsCd11b, integrin alpha-M, integrin, alpha M
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Scientific DescriptionThe principal use of this antibody is in the study of functional heterogeneity of macrophages; it may be used to follow macrophage differentiation and to investigate the function of the CD11b/c equivalent antigen.
- ReactivityRat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Tang HY, Wang FJ, Ma JL, et al. Acupuncture attenuates the development of diabetic peripheral neuralgia by regulating P2X4 expression and inflammation in rat spinal microglia. J Physiol Sci. 2020,70(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12576-020-00769-8Read this paper
- Bonfante R, Napimoga MH, Macedo CG, et al. The P2X7 Receptor, Cathepsin S and Fractalkine in the Trigeminal Subnucleus Caudalis Signal Persistent Hypernociception in Temporomandibular Rat Joints. Neuroscience. 2018,391:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.09.005Read this paper
- Nakajima H, Uchida K, Guerrero AR, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells promotes an alternative pathway of macrophage activation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012,29(8):1614-25. doi: 10.1089/neu.2011.2109Read this paper

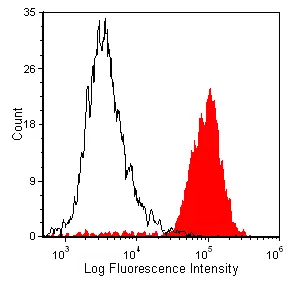
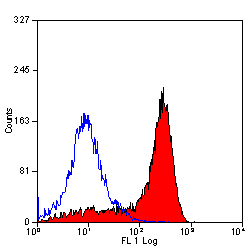
![FACS analysis of rat peritoneal macrophages using GTX76060 CD11b antibody [OX-42].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX76060/GTX76060_352_FACS_w_23061322_471.webp)
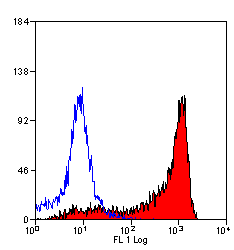
![IHC-Fr analysis of rat lymph node tissue using GTX76357 CD11b antibody [ED7].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX76357/GTX76357_283_IHC-Fr_w_23061322_842.webp)