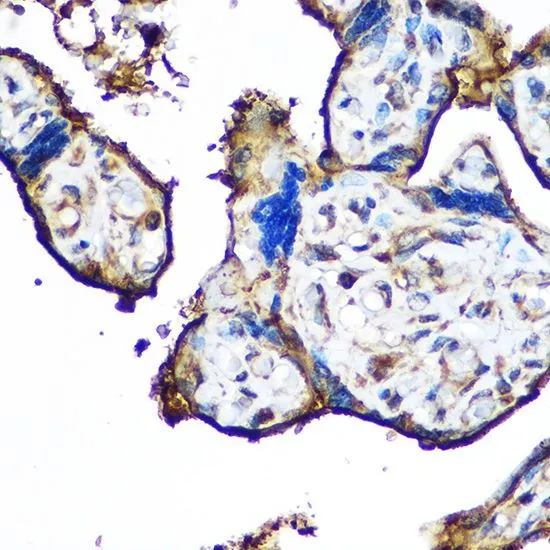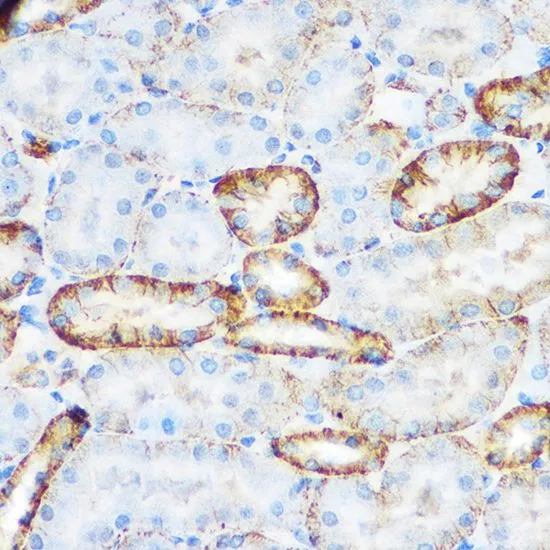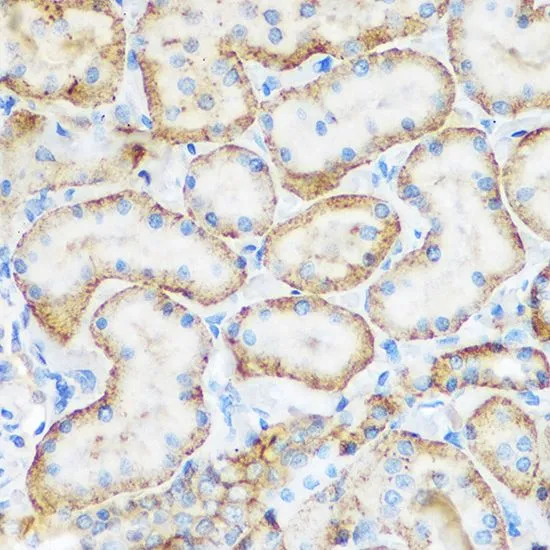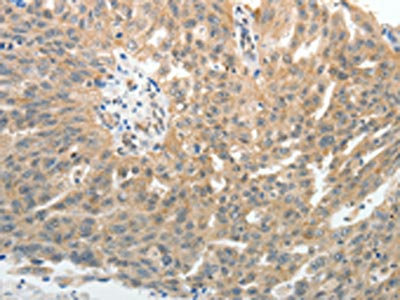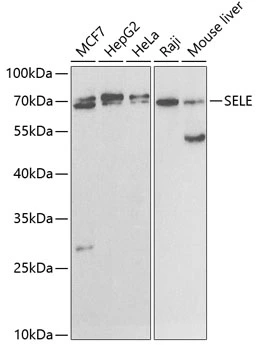
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX54691 CD62E antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
CD62E antibody
GTX54691
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetSELE
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD62E antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6401
- Target nameSELE
- Target descriptionselectin E
- Target synonymsCD62E, ELAM, ELAM1, ESEL, LECAM2, selectin-e, E-selectin, CD62 antigen-like family member E, ELAM-1, endothelial adhesion molecule 1, endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1, leukocyte endothelial cell adhesion molecule 2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP16581
- Protein NameE-selectin
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is found in cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells and is thought to be responsible for the accumulation of blood leukocytes at sites of inflammation by mediating the adhesion of cells to the vascular lining. It exhibits structural features such as the presence of lectin- and EGF-like domains followed by short consensus repeat (SCR) domains that contain 6 conserved cysteine residues. These proteins are part of the selectin family of cell adhesion molecules. Adhesion molecules participate in the interaction between leukocytes and the endothelium and appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Punicalagin Attenuates Disturbed Flow-Induced Vascular Dysfunction by Inhibiting Force-Specific Activation of Smad1/5. Anwaier G et al., 2021, Front Cell Dev BiolRead this paper
- Flavanol metabolites reduce monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells through modulation of expression of genes via p38-MAPK and p65-Nf-kB pathways. Claude S et al., 2014 May, Mol Nutr Food ResRead this paper